wifi connects to laptop but not phone

Title: WiFi Connected But No Internet Access on Windows 11 Fix
Channel: The Geek Page
WiFi Connected But No Internet Access on Windows 11 Fix by The Geek Page
wifi connects to laptop but not phone, why can i connect to wifi on my phone but not my laptop, wifi won't connect to laptop but connects to phone, why does the wifi work on my laptop but not my phone
Wifi: Laptop YES, Phone NO?! The SHOCKING Fix!
Wi-Fi Woes: Laptop Bliss, Phone Blues? Unearthing the Unexpected Solution!
Have you ever experienced the frustrating digital divide? Your laptop streams flawlessly, yet your phone struggles to load a simple webpage. It’s the Wi-Fi paradox. You are left scratching your head. This scenario is more common than you might think. It can be incredibly perplexing.
Decoding the Digital Dilemma: Why the Disconnect?
Imagine this: you are settled on your sofa. Your laptop is happily downloading files. Your phone is buffering endlessly. This discrepancy is not necessarily a sign of a broken device. Instead, it is a symptom. It points to a potential underlying cause. So, let's explore the potential culprits. Firstly, are you positioned correctly? Secondly, are your devices configured optimally?
The Signal Strength Struggle: Location, Location, Location!
The physical location of your devices can vary. The distance from your router is critical. However, the materials surrounding your devices matter, too. Walls and furniture can be Wi-Fi kryptonite. They can severely weaken your signal. Therefore, consider your surroundings. In other words, try moving. Your phone might experience a different outcome. Place both devices next to each other. Is there a difference? If so, consider your phone's position.
Router Roulette: Channel Surfing for Superior Signals
Routers transmit on different channels. These channels can become congested. Other devices can interfere. Essentially, it’s like a radio. A crowded channel means poor reception. So, how do you fix this? You need a Wi-Fi analyzer app. These apps can help you identify which channels are less crowded. Afterward, you can change your router settings. The process is easy. This adjustment might transform your phone's Wi-Fi.
Device Specifics: The Hidden Culprits Unveiled
Let’s examine your devices. The problem isn’t always the Wi-Fi. Sometimes, it’s your phone itself. Older phone models may have outdated Wi-Fi antennas. These can limit their ability to connect. Modern phones often have advanced antenna technology. They may handle Wi-Fi more effectively. Furthermore, phone software can play a role. Consider checking for software updates. These updates can sometimes improve Wi-Fi performance.
Power Saving Paradox: The Battery's Impact on Wi-Fi
Here's another factor to consider. Your phone's power-saving features can impact Wi-Fi. To conserve battery, some phones throttle Wi-Fi. They limit its performance. Hence, disable power-saving modes temporarily. Then, re-test your Wi-Fi connection. This will help you to see if the problem is solved.
The Router Reset Remedy: A Simple Solution
Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the best. Restarting your router is a tried-and-true method. It can often resolve Wi-Fi issues. Turn off your router for a full minute. Afterwards, turn it back on. Give it a few minutes to reboot. Then, check both your laptop and phone. This action often resolves common glitches.
Unmasking the Bandwidth Bottleneck: 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz
Routers broadcast on two different frequency bands. These are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band offers wider coverage. However, it can be slower. The 5 GHz band gives faster speeds. But, it has a shorter range. Most modern phones support 5 GHz. This generally translates to a faster connection. To benefit, your phone and router should be compatible. Check the settings on your phone. Then, connect to the 5 GHz network.
The Shocking Solution: Prioritizing Your Phone's Wi-Fi
Here’s an unexpected tip. Your router may have Quality of Service (QoS) settings. These settings prioritize bandwidth. You can potentially adjust these settings. Give your phone's Wi-Fi more bandwidth in the router settings. This can dramatically improve performance.
Troubleshooting Triumph: A Step-by-Step Guide
First, start basic. Check distance. Then, check router placement again. After that, switch to 5 GHz. Next, restart everything. Consider checking for device updates. Assess your phone’s settings. Additionally, try temporarily disabling power-saving. Finally, investigate QoS settings. If all these steps don't help, then the hardware might be failing.
Conclusion: Mastering the Wi-Fi Universe
Ultimately, the Wi-Fi paradox is solvable. It requires a bit of detective work. By following these steps, you can find the solution. You'll reclaim your digital life. Enjoy seamless Wi-Fi on both your laptop and phone.
Laptop WiFi Broadcasting: The SHOCKINGLY Simple Trick!Wifi: Laptop YES, Phone NO?! The SHOCKING Fix!
Hey tech-savvy friends! Ever been in that frustrating situation? Your laptop’s cruising along, streaming HD movies like a champ, while your phone is sputtering and wheezing, barely managing to load a single Instagram pic? I've been there – more times than I care to admit! We're talking the dreaded "Wi-Fi connected, but no internet" blues. It's like having a brand-new, shiny Ferrari, but the gas tank is stubbornly empty. So, why does Wi-Fi sometimes favor our laptops over our phones? Get ready for a deep dive, because we are about to unearth the shocking fix!
1. The Digital Tug-of-War: Understanding the Problem
Let's paint a picture. You're sprawled on the couch, excited to binge-watch the newest season of your favorite show. Laptop? Zero issues. Phone? Buffering… buffering… a spinning wheel of doom. This isn't just a minor inconvenience; it's a digital tug-of-war, and your phone is losing. What's happening under the hood?
2. Signal Strength: The First Culprit
Think of Wi-Fi signals like whispers. Your router is the person whispering, and your devices are the listeners. The closer you are to the router, the clearer the whisper. But distance isn’t the only factor. Walls, furniture, and even other electronic devices can act as noise, muffling the signal. Your laptop, often equipped with a beefier antenna, might be better at hearing those whispers than your phone, which has a smaller, more sensitive ear.
3. The Router's Role: Traffic Control
The router acts as a digital traffic controller, managing the flow of data to all your connected devices. Imagine a busy highway. If too many cars (devices) are trying to use the same lane (Wi-Fi channel) simultaneously, things slow down. Your router might be giving preference to certain devices (perhaps the ones using more bandwidth, like a laptop streaming video), unintentionally starving your phone.
4. Channel Congestion: The Digital Gridlock
Wi-Fi operates on various channels, like radio stations. If your router is using a congested channel (one that's also being used by your neighbors' routers), it's akin to yelling over a crowded room. Finding a less-crowded channel can be a simple, yet effective solution.
5. Device-Specific Settings: The Hidden Configuration
Your phone and laptop may have different power-saving settings. Your phone, desperate to conserve battery life, might be more aggressive in putting its Wi-Fi into a low-power mode, reducing its ability to maintain a robust connection. Check those battery settings!
6. The Bandwidth Battle: 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz
Routers often broadcast on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. 2.4 GHz has a longer range but is more prone to interference. 5 GHz offers faster speeds but has a shorter range. If your phone is further from the router, it might be clinging to the weaker 2.4 GHz signal, while your laptop is happily connected to the faster 5 GHz.
7. Let's Talk Firmware: Router's Digital Brain
Just like your phone, your router has software (firmware) that needs to be updated. An outdated firmware can lead to all sorts of performance issues, including uneven Wi-Fi distribution. Think of it as a doctor who hasn't kept up with the latest medical advancements – not ideal!
8. Prioritization Protocols: The Wi-Fi Hierarchy
Some routers employ prioritization protocols, also known as Quality of Service (QoS). These protocols allocate bandwidth based on device type or application. Maybe your router, set up by default, favors the laptop for streaming over your phone's casual web browsing.
9. Restarting: The Simple (But Often Overlooked) Fix
Okay, I know, it sounds cliché, but have you tried turning it off and on again? Restarting your router, phone, and laptop can often clear up minor glitches that are causing the problem. It's like a digital reset button.
10. Channel Hopping: Finding the Sweet Spot
As mentioned earlier, your router's channel settings can make a world of difference. Most routers automatically select the best channel, but sometimes they need a nudge. Access your router's settings (usually through a web browser) and try switching to a different channel. There are plenty of apps (for both Android and iOS) that can scan your network and suggest the least congested channels.
11. Device Placement: Strategic Routing
Think of your router as the sun and your devices as plants. They need direct "sunlight" (Wi-Fi signal) to thrive. Try placing your router in a central location, away from walls and obstructions. And try moving your phone closer to the router to see if that solves it.
12. Password Purgatory: Security's Impact
A strong Wi-Fi password is crucial, but sometimes, excessive security protocols can impact device performance. This isn’t common, but outdated security settings on your router could create compatibility issues. Making sure that all your devices support your router’s security type is a good idea.
13. Checking Device Limits: Are You Overloaded?
Most routers impose a limit on the number of devices that can connect simultaneously. Depending on the router, this can limit the bandwith distribution. Consider that, and if your router is outdated, consider changing the device limits or upgrading your router.
14. Diagnosing the Problem: A Step-by-Step Guide
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty. Here’s a simple checklist to troubleshoot:
- Restart Everything: Router, phone, and laptop.
- Check Signal Strength: Is your phone getting a weak signal?
- Test Other Devices: Do other phones/devices have the same issue? If so, it's likely a router problem.
- Change Channels: Access your router’s settings and try different Wi-Fi channels.
- Update Firmware: Ensure your router's firmware is up to date.
- Check Device Settings: Make sure your phone isn’t overly aggressive with power-saving settings.
15. The Ultimate Solution: The Shocking Fix Revealed! (And It's Not What You Think!)
The “shocking” fix isn't some super-secret tech hack. It's about… understanding. Understanding the principles of Wi-Fi, and systematically eliminating potential causes. While there's no single silver bullet, by methodically working through the steps above – checking signal strength, restarting devices, changing channels, and updating firmware – you'll find the answer. It won’t always be a quick fix, but by isolating the issue, you will be able to resolve it. In some cases, it might be time for a router upgrade. Consider that if your router is several years old, you might be missing out on significant performance improvements.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Wi-Fi!
We've covered a lot of ground! From signal strength to channel congestion, we've delved into the reasons why your laptop might be enjoying faster Wi-Fi than your phone. Remember, the goal is to regain control – to become the Wi-Fi master of your domain. Don't let those spinning wheels of doom get the best of you! By following the simple steps outlined above, you can troubleshoot and fix your Wi-Fi woes, ensuring that all your devices can connect seamlessly to the internet. Now, go forth and conquer!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
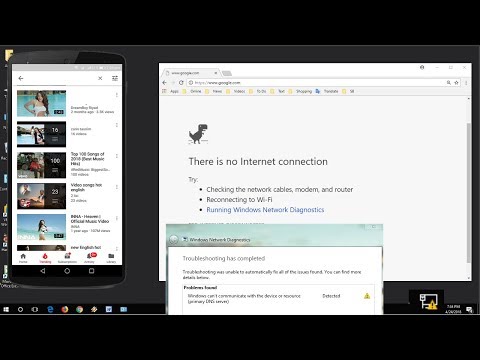
1. Why does my phone’s Wi-Fi say it's connected, but I can’t browse the internet?
This is a common issue! It usually indicates a problem with the connection between your phone and the wider internet. Try restarting your phone and router. Check your router’s settings for any unusual configurations, and also check your DNS settings.
2. How do I find the best Wi-Fi channel for my router?
Download a Wi-Fi analyzer app (available on both Android and iOS). These apps scan your network and recommend the least congested channels. Access your router’s settings (usually through a web browser) and manually select the recommended channel.
3. Should I use 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
5 GHz offers faster speeds but has a shorter range. 2.4 GHz has a longer range but is more prone to interference. If your phone is close to the router, try 5 GHz. If not, 2.4 GHz might be better. If you are not sure, you can connect to both, although make sure you pick the one whose speed is most convenient to you.
4. My laptop and phone are close to the router, but my phone is still slow. What else can I try?
Check your phone’s power-saving settings. Disable Wi-Fi power saving if enabled. Also, consider restarting your phone. Check your router’s firmware and ensure it’s up to date.
5. When should I upgrade my router?
If your router is several years old, it might be time for an upgrade. Newer routers offer improved performance, better security, and support for the latest Wi-Fi standards (like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E). If you constantly experience Wi-
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? This FIX Works EVERY Time!Wi-Fi connected on phone but not working on laptop Solved

By DD TechTV Wi-Fi connected on phone but not working on laptop Solved by DD TechTV
How to Fix No internet, secured in Windows 11

By NETVN82 How to Fix No internet, secured in Windows 11 by NETVN82
Internet Coming In Phone But Not in PCLaptop Solved
By MJ Tube Internet Coming In Phone But Not in PCLaptop Solved by MJ Tube
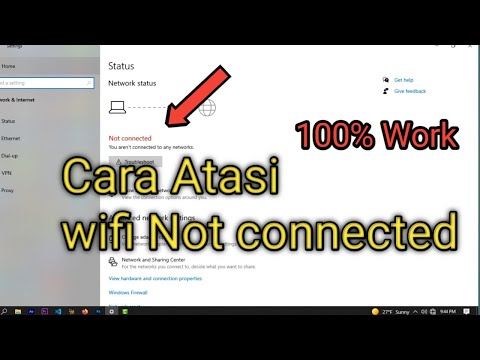
Title: Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected
Channel: ijal tutorial
Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected by ijal tutorial
My Laptop Work
Wifi: Laptop YES, Phone NO?! The SHOCKING Fix!
The modern world hums with the invisible energy of Wi-Fi, connecting us to a universe of information and experiences. Yet, this ubiquitous connectivity can often be maddeningly inconsistent. The frustrating scenario of a laptop effortlessly streaming HD video while a smartphone stubbornly refuses to load a simple webpage is a common, and often infuriating, experience. We delve into the unexpected reasons behind this digital dichotomy and, most importantly, provide the solutions to banish those Wi-Fi woes. Stop pulling your hair out – read on for the liberating fixes!
Decoding the Digital Dance: Why Your Laptop Succeeds Where Your Phone Fails
The disparity between laptop and phone Wi-Fi performance isn't merely a matter of chance; it's a confluence of several technical factors that often conspire against your mobile device. Understanding these nuances allows us to diagnose the problem and, in turn, implement the appropriate remedies. Size, power, and operational priorities play key roles.
Antenna Advantage: The Laptop's Superior Signal Strength
Laptops, by their very design, enjoy a distinct advantage. Their larger chassis accommodates significantly more expansive and sophisticated antenna systems. These antennas are often strategically placed to optimize signal reception and transmission. They have the space to house multiple antennas, often operating on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands simultaneously, allowing for frequency diversity and improved reliability. Smartphones, on the other hand, are constrained by their compact form factor. Their antennas are miniaturized, crammed into limited space, and often struggle to compete with the robust systems found in laptops. This translates into weaker signal reception, resulting in slower data transfer rates and a higher likelihood of dropped connections. This structural difference represents the foundation of the problem.
Power Play: Battery Life vs. Signal Integrity
Power management is a paramount concern for smartphone manufacturers. Every milliampere drained from the battery equates to reduced uptime. To conserve energy, smartphones often employ aggressive power-saving strategies that can, inadvertently, compromise Wi-Fi performance. This might involve reducing the antenna's output power, limiting the number of simultaneous connections, or prioritizing cellular data over Wi-Fi in certain situations. Laptops, plugged into a power outlet or boasting larger batteries, are less constrained by these power-saving measures. Their Wi-Fi adapters can operate at higher power levels, resulting in stronger signals and more stable connections. This fundamental difference in power management practices creates a notable variance in performance.
Bandwidth Battles: Contention for the Digital Airwaves
Wi-Fi routers operate on specific frequency bands, most commonly the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band, while offering longer range, is also prone to congestion. Many devices, including microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and older Wi-Fi routers, operate on this band, creating interference that can significantly degrade performance. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less congestion, but its range is often shorter. Smartphones, especially older models, may not fully support the 5 GHz band, or they may struggle to maintain a strong connection on this band due to their antenna limitations. Laptops, with their superior antenna systems, are often better equipped to handle the challenges of both bands, allowing them to negotiate the most efficient connection.
Software Secrets: The Smartphone's Hidden Hand
Operating system and driver software can also play a crucial role. Smartphone manufacturers often customize the Wi-Fi drivers to optimize performance within the constraints of their hardware. These optimizations, while intended to improve the user experience, can sometimes lead to unexpected compatibility issues or performance bottlenecks. Laptops, benefiting from more standardized hardware and mature drivers, tend to be less susceptible to these types of software-related problems. The specific software implementation can have a notable impact on the overall Wi-Fi experience.
The Ultimate Fixes: Reclaiming Your Wi-Fi Freedom
Now that we understand the underlying causes of Wi-Fi performance discrepancies, we can move onto the practical solutions. Implement these strategies to bring your smartphone's Wi-Fi experience in line with your laptop's.
Router Reboot and Optimization: The Foundation of a Strong Connection
Before undertaking more complex troubleshooting steps, start with the simplest solution: reboot your router. Unplug the router from its power source, wait for at least 30 seconds, and then plug it back in. This simple action can clear temporary glitches and refresh the router's internal processes, improving connectivity.
Next, ensure your router firmware is up to date. Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that include bug fixes, performance improvements, and security enhancements. Check your router's administration panel (usually accessed through a web browser) for available updates and install them.
Finally, optimize your router's settings. Access your router's administration panel and configure the following settings:
- Channel Selection: Avoid using the default "Auto" channel selection. Instead, manually select a less congested channel. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (available for both smartphones and laptops) to identify the least crowded channels in your area. For the 2.4 GHz band, channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally recommended, as they do not overlap. For the 5 GHz band, select a channel that offers the best performance in your environment.
- Channel Width: For the 5 GHz band, enable the use of 80 MHz or higher channel widths, if supported by your devices, to achieve faster speeds.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Most routers offer QoS settings that prioritize certain types of network traffic. If your router supports it, configure QoS to prioritize Wi-Fi traffic from your smartphone.
Smartphone Specific Tweaks: Fine-Tuning Your Mobile Connection
Beyond your router, there are several adjustments you can make directly on your smartphone to enhance its Wi-Fi performance:
- Forget and Reconnect: Try "forgetting" the Wi-Fi network on your phone and then reconnecting. This can refresh the network settings and resolve any configuration errors. Go to your phone's Wi-Fi settings, tap on the network name, and select "Forget." Then, reconnect to the network and enter the password.
- Disable Wi-Fi Power Saving Mode: Some smartphones offer a Wi-Fi power-saving mode that can reduce performance. Disable this mode in your phone's Wi-Fi settings or advanced settings. This may be labeled differently depending on your phone model and Android variant (e.g., "Wi-Fi optimization," "Smart Wi-Fi").
- Location Services: Sometimes, location services can interfere with Wi-Fi performance. Try disabling location services temporarily to see if it improves connectivity. Go to your phone's location settings and disable location services for Wi-Fi scanning or all apps.
- Disable Bluetooth: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi often operate on the same 2.4 GHz frequency band, so they can interfere with each other. Temporarily disable Bluetooth to see if it improves your Wi-Fi connection.
- Software Updates: Ensure your phone's operating system and Wi-Fi drivers are up to date. Check for updates in your phone's settings. Outdated software can sometimes lead to compatibility issues and performance problems.
Hardware Considerations: Expanding Your Wi-Fi Reach
In more complex environments, such as large homes or buildings with thick walls, you may need to consider hardware solutions to improve Wi-Fi coverage and performance:
- Wi-Fi Extenders: Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters can be used to amplify the Wi-Fi signal and extend its range. Place the extender halfway between your router and the area with poor Wi-Fi coverage. Select an extender that supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands and that uses the latest Wi-Fi standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) for optimal performance.
- Mesh Wi-Fi Systems: Mesh Wi-Fi systems offer a more comprehensive solution for expanding Wi-Fi coverage. These systems consist of multiple nodes that work together to create a single, seamless Wi-Fi network throughout your home. Place the nodes strategically to ensure even coverage.
- Router Upgrades: If your existing router is outdated or unable to handle the demands of your network, consider upgrading to a newer model. Look for a router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E) and that offers features like MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) and beamforming for improved performance.
Troubleshooting Techniques: Diagnosing Persistent Problems
If you have implemented the above solutions and are still experiencing Wi-Fi issues, try the following troubleshooting techniques:
- Test with Different Devices: Connect other devices (laptops, tablets, etc.) to your Wi-Fi network to determine if the problem is specific to your smartphone. If other devices are experiencing similar issues, the problem is likely with your router or the network connection itself.
- Test in Different Locations: Move your smartphone to different locations within your home to assess the signal strength and identify any dead spots.
- Factory Reset: As a last resort, try factory resetting your smartphone. This will erase all data on your phone, so be sure to back up your important files before performing a factory reset. Go to your phone's settings, find the "Reset" or "Backup & Reset" option, and select "Factory data reset."
- Contact Your Internet Service Provider: If you have exhausted all other troubleshooting steps, contact your internet service provider (ISP) to rule out any problems with your internet connection. They may be able to diagnose the problem remotely or schedule a technician visit
