how to test laptop wifi card
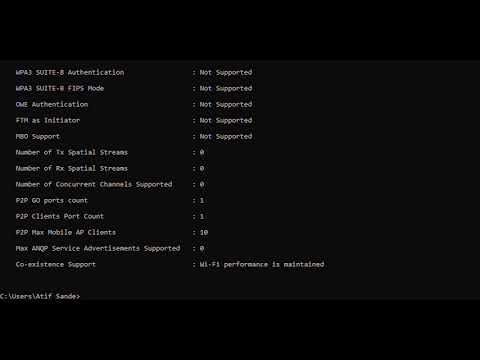
Title: How To Check Inbuild Wi-Fi Card Supports Monitor Mode With cmd In Windows 10
Channel: EtHaRay
How To Check Inbuild Wi-Fi Card Supports Monitor Mode With cmd In Windows 10 by EtHaRay
how to test laptop wifi card, how to check laptop wifi card, how to check laptop wifi card speed, how to test your laptop wifi card, how to check if laptop wifi card is working, how to check my laptop wifi card, how to check your laptop wifi card, how to check laptop wireless network card, how to check if laptop has wifi card, how do i know if my laptop wifi card is bad
Is Your Laptop WiFi Dying? This SHOCKING Test Will Reveal ALL!
Is Your Laptop's WiFi a Digital Ghost? Unmasking the Truth!
It's a familiar scenario, isn't it? You're in the middle of something crucial – maybe a video call, streaming your favorite show, or finalizing a work project – and then it happens. The dreaded buffering symbol appears, the connection lags, and your laptop's WiFi seems to have vanished into thin air. This can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you need a reliable connection. But what if I told you there's a way to unveil the truth about your WiFi woes, to see if your laptop’s wireless capabilities are truly on their last legs?
Decoding the WiFi Whisper: Initial Symptoms and Suspicions
Before we dive into the tests, let's first establish some common warning signs. After all, recognizing the early indications of a weakening WiFi signal is key. Does your internet feel sluggish? Are websites loading at a glacial pace? Do you often experience dropped connections, especially when you're further away from your router? These are all potential clues. These symptoms could indicate a deeper issue. You might also notice a general decline in download and upload speeds. In fact, even seemingly minor hiccups can be telltale signs. Consequently, before you blame your internet provider, it's wise to investigate your laptop.
The WiFi Detective: Simple Diagnostic Steps
The good news is, you don't need to be a tech guru to troubleshoot your WiFi. In fact, there are several easy steps you can take to get a clearer picture. First, try a quick restart. Rebooting your laptop is surprisingly effective at resolving many minor issues. Secondly, check your router. Is it functioning correctly? Sometimes, simply restarting your router can work wonders. Thirdly, move closer to your router. This can immediately eliminate some potential problems.
A Shocking Revelation! The Hidden WiFi Test
Now, for the main event. The test that promises to reveal the truth. It is designed to expose any weaknesses the WiFi system may have. Moreover, it is surprisingly simple. First, open your laptop's command prompt. You can find this by searching for "cmd" in your search bar. Once the command prompt window opens, type "ping google.com -t" and press enter. What this does is send a continuous stream of data packets to Google’s servers. Hence, we can monitor your connection’s performance.
Interpreting the Results: Unveiling the Truth
After running the ping test for a few minutes, observe the results. You'll want to look for a few key indicators. First, pay close attention to the "time" values. These numbers represent the latency, or the time it takes for the data packets to travel to Google and back. Ideally, you want to see low "time" values. Elevated "time" values, especially those consistently above 100ms, could flag connection issues.
Secondly, look for “Request timed out” messages. These indicate lost packets. This usually represents a problem. A few lost packets are normal, but a high percentage of packets being lost signals trouble. It therefore strongly denotes potential WiFi signal problems. Finally, check for consistent patterns. Consistent high latency or frequent packet loss suggests that your WiFi may be underperforming.
Beyond the Test: Troubleshooting and Solutions
If the test reveals problems, don't despair! In fact, there are several steps you can take to improve your WiFi performance. First, consider the physical environment. WiFi signals can be easily obstructed. Walls, appliances, and even some furniture can interfere with the signal. Secondly, try updating your network drivers. Keeping your network drivers up-to-date can resolve compatibility issues. Thirdly, consider upgrading your router. Older routers may struggle to handle modern internet speeds.
The Final Verdict: Is Your Laptop's WiFi Doomed?
Ultimately, the ping test is a powerful diagnostic tool. It can provide critical insights into your WiFi's health and performance. In short, it’s a solid tool. If your laptop’s WiFi is struggling, the test helps you identify and resolve those issues. Furthermore, it helps you avoid the frustration of a constantly unreliable connection. So, run the test. Uncover the secrets of your WiFi. Know for certain.
Laptop Wi-Fi MIA? This SHOCKING Trick Finds It INSTANTLY!Is Your Laptop WiFi Dying? This SHOCKING Test Will Reveal ALL!
Hey there, fellow tech travelers! Ever feel like your laptop's WiFi is moving at the speed of a snail in molasses? One minute you're streaming your fave show, the next you're staring at the spinning wheel of doom, wondering if your connection has packed its bags and gone on an extended vacation. We've all been there! And frankly, it’s frustrating! But before you chuck your trusty laptop out the window (tempting, I know!), let's figure out what's really going on. Is your WiFi just being a little temperamental, or is it facing a slow, agonizing demise? We’re going to unearth the truth with some simple, surprising tests.
1. The WiFi Whirlwind: What's Really Happening?
Think of your WiFi as a busy highway. Your laptop (and your other devices) are cars, and the data is the traffic. Now, what happens when there's a traffic jam? You slow down, right? Well, the same thing can happen with your WiFi. Interference, distance from the router, and the number of devices hogging the bandwidth can all contribute to a sluggish experience. But sometimes, it’s more than just traffic. It could be a problem with your laptop's WiFi adapter itself. Imagine a car with a faulty engine – it's going to struggle, no matter how clear the road is.
2. The "Speed Test" Showdown: Your First Line of Defense
Okay, let’s get practical. The first thing we always do is a speed test. It's our basic "check engine" light for your WiFi. There are tons of free speed test websites out there (Speedtest.net and Fast.com are solid choices). Simply visit one, hit the "go" button, and let it run. What you're looking for are your download and upload speeds. Note them down. Keep the results.
- What to look for: Does your download speed match what your internet provider promised? If you're supposed to get 100 Mbps and you're getting 10, that's a major red flag.
- What’s considered "good": Generally, for streaming and basic browsing, anything above 25 Mbps download is decent. For more demanding tasks, like online gaming or video editing, you'll want much higher speeds.
- Important Note: Run the test several times. WiFi can fluctuate, and a one-off slow test doesn't necessarily mean your WiFi is dying.
3. The Router Reconnaissance: Is It The Culprit?
Let's not jump to conclusions about your laptop just yet. Sometimes, the problem lies not with the car (your laptop) but with the highway itself (your router). Routers can get overloaded or experience glitches.
- The Quick Fix: The first thing to try is the good old "unplug it and plug it back in" trick. Seriously! Unplug your router (and your modem, if they’re separate) for about 30 seconds, then plug them back in. This often clears minor issues. Think of it like hitting the reset button on your brain after a long day.
- The Location Factor: Is your router tucked away in a closet or behind a wall of books? Radio waves don't like obstacles! Try moving your router to a more central, open location in your home.
- The Upgrade Question: Is your router ancient? Technology moves fast. An old router might not be able to handle the demands of modern internet usage. If you're still using a router from the early 2010s, it might be time for an upgrade.
4. The "Windows Troubleshooter" Wrangle: Let Microsoft Lend a Hand
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter designed to fix common network problems. It’s like having a tech support guru right at your fingertips (minus the phone call wait times!).
- How to access it: Type "network troubleshooter" into the Windows search bar. Click on the result.
- Let it work its magic: Follow the on-screen prompts. The troubleshooter will scan for issues and, hopefully, offer a solution. It's surprisingly effective! Think of it like visiting a doctor to know the cause of the issues.
5. The WiFi Adapter Audit: Delving into Device Manager
Now, we're getting closer to the truth about your laptop's WiFi adapter. Open Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar).
- Locate your network adapter: Expand the "Network adapters" section. You should see your WiFi adapter listed (it might say something like "Intel Wireless-AC 9560" or similar).
- Check for error messages: If there's a yellow exclamation mark next to your adapter, that's a problem. Right-click on the adapter and select "Properties." Look for any error messages in the "Device status" section.
- Update the driver: Right-click the adapter and select "Update driver." Choose to search automatically for updated drivers. This is like giving your car's engine a tune-up.
- Disable and re-enable: If updating the driver doesn’t work, try disabling the adapter (right-click, "Disable device") and then re-enabling it (right-click, "Enable device").
6. The "Ping Test" Plunge: Measuring Network Latency
A "ping" is a network utility that sends a tiny data packet to a website (like Google.com) and measures how long it takes to get a response. This is a great way to gauge the latency of your connection – basically, how quickly your laptop can "talk" to the internet.
- How to do it: Open the Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar). Type
ping google.comand press Enter. - What to look for: The results will show you the minimum, maximum, and average "time" (in milliseconds or ms) it took for the packets to travel. Lower numbers are better. Anything consistently above 100ms could indicate a problem.
- Interpreting the Results: High ping times can lead to lag in online games, slow webpage loading, and generally a sluggish feeling.
7. The Channel Changer: Navigating the WiFi Airwaves
Just like radio stations, WiFi routers broadcast on different "channels." Sometimes, these channels can get congested, especially in apartment buildings or densely populated areas.
- Finding the Best Channel: Most routers automatically select the best channel, but sometimes it's worth manually checking. There are free apps for your phone (like WiFi Analyzer) that can show you which channels are least crowded.
- Changing the Channel: Log in to your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser – you can find the IP address in your router's documentation). Look for the WiFi settings and the "Channel" option. Experiment with different channels to see if it improves your performance.
8. The "Physical Proximity Probe": The Ultimate Test
Alright, let’s get physical. Move your laptop very close to your router. Like, right next to it. Run a speed test again.
- If the speed improves dramatically: This suggests the problem is likely related to distance or interference. Consider moving your router to a better location or using a WiFi extender to boost the signal.
- If the speed doesn't improve: This points to a potential issue with your laptop's WiFi adapter itself. It could be damaged or malfunctioning.
9. The "Other Devices" Experiment: Isolating the Issue
Let's try to isolate the problem. Do other devices (your phone, another laptop, a tablet) also experience slow WiFi?
- If all devices are slow: The problem is likely with your internet service, router, or overall network environment.
- If only your laptop is slow: The issue is probably specific to your laptop's WiFi adapter.
10. The "External Adapter" Alternative: A Temporary Fix
If you suspect your laptop's WiFi adapter is the culprit, you can try using an external USB WiFi adapter. These are inexpensive devices that plug into your laptop's USB port and provide a separate WiFi connection.
- Testing it out: Disable your built-in WiFi adapter in Device Manager (as described above). Plug in the external adapter. Connect to your WiFi network through the new adapter.
- If the external adapter works better: This strongly suggests that your built-in adapter is failing. Consider replacing it or using the external adapter as a long-term solution.
11. The "Reset Network Settings" Ritual: A Drastic Measure
This is a more involved step, so proceed with caution! Resetting your network settings in Windows can sometimes resolve difficult WiFi issues. This will essentially reset your network configuration to its default settings.
- How to do it: Go to Settings -> Network & Internet -> Advanced network settings -> Network reset.
- What to expect: You'll lose any custom network settings you've configured. You may need to re-enter your WiFi password. It’s a bit like hitting the "undo" button on all your network customizations.
12. The "Factory Reset" Finale: The Nuclear Option
This is a last resort! A factory
Laptop WiFi MIA? Windows 10 Fix Inside!Upgrade to INTEL AX210 WIFI 6E Card on LAPTOP... 1.2GBPS

By Zaim Afham Upgrade to INTEL AX210 WIFI 6E Card on LAPTOP... 1.2GBPS by Zaim Afham
WiFI Card vs USB WiFi Adapter Check out this comparison

By ADVANTI WiFI Card vs USB WiFi Adapter Check out this comparison by ADVANTI
How to Know if My Desktop PC Is Equipped for Wireless Know Your Computer

By eHowTech How to Know if My Desktop PC Is Equipped for Wireless Know Your Computer by eHowTech
Title: How to Tell if the Wireless Card Is Dead in My HP Laptop Tech Vice
Channel: eHowTech
How to Tell if the Wireless Card Is Dead in My HP Laptop Tech Vice by eHowTech
Laptop Wifi Connect
Is Your Laptop WiFi Dying? This SHOCKING Test Will Reveal ALL!
We've all been there: staring at a spinning wheel, a buffering screen, or a frustratingly slow download while our patience wears thin. The culprit? Often, a faltering Wi-Fi connection. But is your laptop's Wi-Fi truly dying a slow death, or is it a simple, easily fixable issue? We’re here to unveil a series of tests, a deep dive into your laptop's wireless capabilities, to determine the true state of your connection. This isn't just about guessing; it's about diagnosing, understanding, and ultimately, regaining control of your online experience.
The Preliminary Examination: Recognizing the Early Warning Signs
Before we launch into technical tests, let's first acknowledge the subtle whispers of a failing Wi-Fi connection. These are the signals that tell us something might be amiss. Recognizing these early warning signs can save you hours of frustration and potentially prevent a complete Wi-Fi collapse.
- Slow Browsing Speeds: This is the most common complaint. Are web pages taking an eternity to load? Do videos constantly buffer? While general internet speed is a factor, consistently slow browsing only when connected to your Wi-Fi is a red flag.
- Intermittent Connection Drops: Does your laptop lose its connection to the Wi-Fi network randomly? This can manifest as short disconnections or complete network dropouts. This could range from some seconds to a few minutes.
- Weak Signal Strength in Close Proximity: Even when you're sitting right next to your router, is your Wi-Fi signal indicated as weak? This is a particularly strong indicator that your laptop’s wireless hardware might be failing.
- Inconsistent Speeds Across Devices: Compare the Wi-Fi performance with other devices, like your phone or another laptop. If other devices are performing well on the same network, your laptop is likely the source of the problem.
- Difficulty Connecting Initially: Does your laptop struggle to connect to the Wi-Fi network in the first place? Does it take unusually long, or does it fail to connect altogether?
If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, it's time to move on to the more specialized tests.
Test 1: The Speed Test Showdown: Unmasking the True Bandwidth
The most immediate and useful test is a simple speed test. But we're not just looking for a number; we're looking for trends. This step allows us to establish a baseline and see how your laptop’s Wi-Fi is truly performing.
- Choose a Reliable Speed Test Method: Use a reputable speed test website. Speedtest.net or fast.com are popular choices. Ensure that you are using the speed test on your laptop, connected to your Wi-Fi network.
- Conduct Multiple Tests: Run the speed test at least three times, spaced a few minutes apart. Note the download speed, upload speed, and ping (latency) for each test. Variations can provide further insight.
- Compare to Wired Connection (if possible): Ideally, connect your laptop directly to your router with an Ethernet cable. Run the same speed tests. This will establish a benchmark for your internet service's maximum potential. Significant differences between wired and wireless speeds point towards a Wi-Fi issue.
- Analyze the Results: If your Wi-Fi download speeds are significantly lower than your wired speeds (or the speeds you expect based on your internet plan) and are inconsistent from test to test, this suggests a problem with your laptop's wireless adapter or connection. If you are experiencing the same speed, that means the issue might be with your internet connection instead of your laptop.
Test 2: The Signal Strength Saga: Measuring the Digital Footprint
Signal strength directly impacts Wi-Fi performance. A weak signal invariably translates to slow speeds and frequent dropouts. We will measure the signal to ascertain the strength.
- Use a Signal Strength Analyzer: Many operating systems provide built-in tools to visualize this. On Windows, click on the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray and hover over your network name. This will often display signal strength in bars or a percentage. Third-party apps like NetSpot (available for both Windows and macOS) provide much more detailed signal strength mapping and analysis.
- Evaluate Signal Strength in Different Locations: Move your laptop around your home or office and observe the signal strength. Does it fluctuate dramatically? Are there areas where the signal is consistently weak? This can help identify dead zones or areas where interference is a problem.
- Look for Interference Sources: Identify potential sources of interference, such as microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and other electronic appliances. Experiment by moving your laptop or the router away from these objects to improve performance.
- Compare Radios: The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands from the router has different characteristics. 2.4 GHz offers better range but can be more susceptible to interference, while 5 GHz offers faster speeds but shorter range. For example, on a Windows PC, you can check your wireless connection in the network and sharing center under the "view connection status" section.
Test 3: The Packet Loss Pursuit: Investigating Data Delivery
Packet loss is a common but often overlooked reason for slow or unreliable Wi-Fi connections. Packet loss occurs when data packets sent over the network fail to reach their destination.
- Use the Ping Command: The "ping" command is a simple and effective way to test for packet loss. Open the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS). Type
ping [your router's IP address]and press Enter. You can usually find your router's IP address in the settings of your laptop. - Run the Ping Test: Let the ping command run for at least a few minutes. Observe the results.
- Analyze the Results: Look for any messages indicating packet loss (e.g., "Request timed out"). If you see packet loss, it indicates a reliability problem with the wireless connection. A significant packet loss rate, even in the single digits, can significantly impact performance.
- Ping a Public Website: Repeat the ping test, but this time, use a website address like Google.com or Cloudflare.com. This tests the connection to the internet in general.
Test 4: Driver Diagnosis: Ensuring the Right Software
Outdated or corrupted Wi-Fi drivers are a common cause of Wi-Fi problems. Your laptop’s wireless adapter won't function properly without the correct drivers.
- Check for Driver Updates: On Windows, go to Device Manager (search for it in the Start menu). Expand "Network adapters." Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers" to let Windows search for the latest version.
- Manually Download Drivers (if needed): If Windows can’t find an update, visit your laptop manufacturer's website or the website of your Wi-Fi adapter manufacturer (e.g., Intel, Broadcom) and download the latest drivers.
- Roll Back Drivers: If you recently updated your drivers and your Wi-Fi performance worsened, you can "roll back" to the previous driver version. In Device Manager, right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver" if the option is available.
Test 5: The Router Revelation: Addressing the Gateway
While the focus is on your laptop, the router is the gateway to your internet connection. Router issues can often be mistaken for laptop Wi-Fi problems.
- Restart Your Router and Modem: This simple step often resolves temporary glitches. Unplug both devices, wait 30 seconds, plug the modem back in, wait for it to fully boot up, and then plug the router back in.
- Check Router Firmware: Outdated router firmware can cause performance and security issues. Access your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into a web browser). Look for a firmware update option and install the latest version.
- Router Placement: Ensure your router is centrally located in your home or office and is not obstructed by walls or objects that could interfere with the signal. Elevating the router can also help.
- Frequency Band Optimization: Most modern routers support dual-band Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). The 5 GHz band is usually faster but has a shorter range. If you are close to the router and need speed, use the 5 GHz; if you need range, use the 2.4 GHz.
Test 6: Hardware Hardcore: Considering the Physical
If all other tests come back and you're still experiencing connection woes, the issue might be with the physical Wi-Fi adapter in your laptop.
- Check for Physical Damage: Inspect your laptop's Wi-Fi card and its antennas for any signs of physical damage.
- External USB Wi-Fi Adapters: If the internal Wi-Fi adapter is suspected, obtain a USB Wi-Fi adapter. If the USB adapter provides a better connection and speed, that verifies your internal Wi-Fi adapter is the culprit.
- Consult a Professional: If you suspect a hardware failure and feel uncomfortable opening your laptop, take it to a qualified computer repair technician.
Interpreting the Results: What Do Your Tests Mean?
Once you’ve completed these tests,
