laptop wifi card pinout
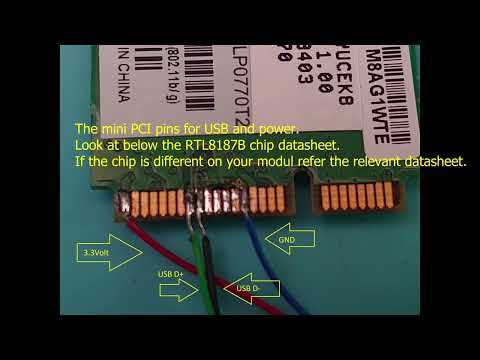
Title: Transform mini pci WiFi to USB
Channel: Anthony Vincz
Transform mini pci WiFi to USB by Anthony Vincz
laptop wifi card pinout, laptop wifi module pinout, laptop wifi card wiring, laptop wifi card not working, laptop wifi card types, laptop wifi card slot types
Laptop WiFi Card Pinout: The Ultimate Guide (With Pictures!)
Unveiling the Secrets: Your Laptop WiFi Card Pinout Decoded (With Visuals!)
Ever felt like you're speaking a foreign language when discussing tech? Well, don't fret; we're about to decipher the cryptic world of laptop WiFi card pinouts. This guide is designed for everyone. We'll demystify the connections that keep you connected.
Decoding the Digital Maze: Why Pinouts Matter
Understanding your laptop's WiFi card pinout is crucial for several reasons. For instance, it's vital for troubleshooting connectivity issues. Moreover, it's essential if you're planning upgrades or repairs. Essentially, pinouts act like a roadmap. They show you where everything connects. This knowledge empowers you to diagnose problems accurately. Furthermore, it facilitates safe and effective modifications.
Getting Acquainted: The WiFi Card Anatomy
Before we dive in, let's familiarize ourselves with the WiFi card. Typically, these cards are small, rectangular circuit boards. They slot into a dedicated mini-PCIe or M.2 slot on your laptop's motherboard. The card itself houses the WiFi chipset. This chipset handles the wireless communication. You'll also find antenna connectors. They often come in the form of U.FL connectors.
The Pinout's Purpose: A Symphony of Signals
Now, let's explore the pinout's purpose. Each pin serves a specific function. These functions are crucial for smooth operation. Each connection carries essential signals. These signals include power, data, and control. Generally, the pinout specifies the voltage requirements. It also dictates the data transfer protocols. Finally, it details the control signals. Understanding this intricate system is vital for any repair.
Unraveling the Mystery: Common Pinout Configurations
Pinouts vary depending on the card type and manufacturer. Consequently, identifying yours is important. However, some common configurations appear frequently. Let's look at some prevalent examples.
Mini PCI-e Pinout: These older cards often have 52 pins. The pinout arrangement is quite specific. It includes power (3.3V and 12V), ground, and various data lines. These data lines are crucial for communication. They also include control signals for enable and disable functions.
M.2 Pinout (Key A/E): These are more modern cards. They primarily use the M.2 form factor. A/E key cards usually have 75 pins. The arrangement still involves power and ground connections. It utilizes PCIe, USB, and other interface lanes. These lanes facilitate high-speed data transfer. Therefore, they ensure optimal performance.
Visual Aids: Pinout Diagrams and Their Significance
Pinout diagrams are your best friend. So try your best to find one. These diagrams are graphical representations of the pin layout. These diagrams visually depict which pins are connected to which components. Furthermore, they show the function of each pin. Always consult the manufacturer's documentation. This information may provide the pinout for your specific model. You can frequently find pinout diagrams online.
Troubleshooting 101: Pinouts in Action
Pinouts are incredibly helpful for troubleshooting. Let's say your WiFi isn't working. First, verify the card is properly seated. Check the pin connections for any visible damage. Also, examine the power supply to the card. Consult the pinout diagram. Then, use a multimeter. Inspect the voltage measurements. Also, ensure that the correct signals are present. This process helps in pinpointing the root cause.
Upgrading Made Easy: Pinouts as Guides
Thinking of upgrading your WiFi card? The pinout becomes even more crucial. Ensure the new card is compatible. It has to fit existing connectors. Study the new card's pinout. Make sure they align with your laptop's slot. Before proceeding, familiarize yourself with the power requirements. You also want to check other critical signals. This will prevent damage during installation.
Safety First: Precautions to Remember
Working with electronics requires caution. Always disconnect power. Moreover, it's crucial before any modifications. Use an anti-static wrist strap. This will protect the components from electrostatic discharge. Also, work in a well-lit area. This environment helps with visual inspection. Take your time. Avoid applying excessive force.
Conclusion: Mastering the WiFi Card Pinout
In conclusion, understanding your laptop's WiFi card pinout empowers you. You can troubleshoot, upgrade, and maintain your connectivity. Remember that pinouts can be complex. Therefore, patience and attention to detail are essential. With the right knowledge, you can navigate the digital maze. You'll be well-equipped to tackle any WiFi-related challenge! Now, you're ready to explore the wonderful world of wireless connectivity!
Find Your Laptop's WiFi MAC Address INSTANTLY! (Secret Trick Inside)Laptop WiFi Card Pinout: The Ultimate Guide (With Pictures!)
Hey tech enthusiasts! Ever stared at your laptop's WiFi card and wondered what all those tiny pins are really doing? Perhaps you're upgrading your card, troubleshooting connectivity issues, or just curious about the inner workings of your digital companion. Well, you've come to the right place. We're diving deep into the fascinating world of the laptop WiFi card pinout, breaking down the mysteries and illuminating the connections that make your internet magic happen. Prepare to have your mind – and your soldering skills – sparked!
Decoding the Digital DNA: What is a WiFi Card Pinout?
Think of the WiFi card pinout as the blueprint of your wireless card. It's the secret map that reveals how each individual pin connects to other components within your laptop, like the motherboard and the antenna. Understanding this "map" is critical if you're ever planning to do anything beyond simply turning your laptop on and hoping for the best. It’s akin to understanding the wiring diagram of your car engine – you wouldn't just start tinkering without it, would you? (Unless you're feeling really adventurous!).
Why Bother? The Perks of WiFi Card Pinout Knowledge
So, why dedicate time to learning something so seemingly technical? Well, the benefits are surprisingly plentiful.
- Troubleshooting Nirvana: If your WiFi is acting up – slow speeds, dropped connections, the dreaded "no internet available" – understanding the pinout can help you pinpoint the problem. Is it a faulty antenna connection? Perhaps a short circuit? The pinout is your technical detective's magnifying glass.
- Upgrade Your Game: Thinking about upgrading your WiFi card to a faster standard (like WiFi 6 or even WiFi 6E, if you're feeling fancy)? Knowing the pinout ensures compatibility and helps you navigate the installation process with the confidence of a seasoned pro.
- DIY Delight (and Potential Risks): Got a broken connector? Perhaps you fancy soldering in a new antenna. The pinout is your best friend. However, before we go any further, a massive disclaimer: This stuff can be delicate, and you could potentially fry your card or even your laptop if you're not careful. Always tread with caution and, if unsure, seek professional help.
- Pure Tech Curiosity: Let's be honest, there's a certain satisfaction in understanding how things work, right? Peeking behind the curtain and understanding the intricate ballet of signals and power within your laptop is genuinely fascinating!
The Anatomy of a Typical Laptop WiFi Card: A Visual Introduction
Before we get our hands dirty with specific pinouts, let's appreciate the WiFi card itself. They're usually miniature marvels, packed with components that perform some seriously complex tasks. They often come in two main form factors:
- M.2 (NGFF): These are the sleek, rectangular cards you'll mostly see in modern laptops. They connect via a standardized M.2 slot and are renowned for their compact design and high performance.
- Mini PCI-e: Older laptops often utilize these slightly larger cards, connecting via a Mini PCI-e slot.
Image Alt Text: A close-up photograph of a M.2 laptop WiFi card illustrating its components such as the antenna connectors, and the gold-plated edge connector.
Image Caption: A typical M.2 WiFi card showing the antenna connections (left), the gold-plated edge connector (right), and other various components (center).
Demystifying the M.2 WiFi Card Pinout
The M.2 form factor is now dominant, so let's start with the most common kind of WiFi card. These cards use an edge connector, a collection of pins that interface with the M.2 slot on your motherboard.
- Power Pins: These pins supply the card with the necessary juice to operate.
- Data Pins: These are the channels for transmitting and receiving Wi-Fi signals to and from the antennas.
- Control Pins: Facilitate the card's communication with the system, managing functions like enabling or disabling the WiFi and overseeing other features.
Important Note: Pinouts can vary slightly between cards, but the core functionality and basic pin assignments tend to be consistent. Always consult the datasheet or technical specifications of the specific card you're working with.
Mini PCI-e WiFi Card Pinout: A Blast From the Past
While less common now, Mini PCI-e cards still pop up in older laptops. Their pinout is somewhat different from M.2.
- Power Pins: Similar to M.2, these pins provide the power supply to the card.
- PCI-e Data Lanes: These are the workhorses, carrying data to and from the card.
- USB Pins: Some Mini PCI-e cards may also feature USB connections.
Image Alt Text: Mini PCI-e laptop WiFi card demonstrating its size and design.
Image Caption: Mini PCI-e WiFi card, slightly older than its M.2 counterpart, exhibiting the pins for connecting to a laptop.
Unveiling the Antenna Connections: The Signal Receivers
These are crucial, because without them, your card is just a fancy piece of plastic. Most WiFi cards have two or three connectors for the antennas, typically utilizing a small push-on connector.
- Connecting to the Antennas: The antenna cables are connected from the WiFi card to the front where the screen is placed.
- Understanding the Connectors: There are different styles of connectors, but they generally attach to the card with a simple push.
Step-by-Step Guide to WiFi Card Replacement (Carefully!)
So you're ready to upgrade your WiFi card? Wonderful! Follow these steps, but with extreme care:
- Power Down: Completely shut down your laptop and unplug the power adapter. Safety first!
- Open It Up: Carefully unscrew and open your laptop's casing. Consult your laptop's manual for the correct procedure.
- Find the WiFi Card: Locate the WiFi card. It's usually easily identifiable.
- Disconnect Antennas: Gently detach the antenna cables from the old card.
- Unscrew the Card: Remove the screw securing the card in place.
- Carefully Remove the Card: Slide the card out of its slot.
- Install the New Card: Insert the new card into the slot and tighten the screw.
- Reconnect Antennas: Reseat the antenna cables onto the new card.
- Close Up Your Laptop: Reassemble your laptop.
- Test and Troubleshoot: Power up your laptop and check for WiFi connectivity. If the WiFi doesn’t work, double-check all connections and refer to online resources.
Common WiFi Card Pinout Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
Even with the best intentions, things can go wrong. Here's how to tackle some common issues:
- No WiFi Detected: Ensure the card is correctly seated in the slot and that the antennas are securely connected. Check the BIOS to see if the WiFi card is enabled.
- Slow Speeds: Verify that the card is compatible with your router's WiFi standard. Check your internet speed.
- Intermittent Connection: Inspect the connections and re-seat the card. Consider that your antenna cables could be damaged.
Advanced Troubleshooting: When to Call in the Professionals
Sometimes, you'll hit a wall. If you've tried everything and still can't get your WiFi to work, consider:
- Card Failure: The card itself might be faulty.
- Motherboard Issues: There could be a problem with the M.2 or Mini PCI-e slot.
- Consulting a Technician: If you're uncomfortable with any of the above steps or the issue persists, hand it over.
Safety First: Preventing Damage
Always remember to take precautions to prevent damage:
- Static Electricity: Ground yourself to prevent static discharge.
- Gentle Approach: Be gentle when handling components.
- Research is Key: Before starting any work, research your specific laptop model.
Useful Resources for WiFi Card Pinout Information
Where should you look for help? Plenty of resources are available:
- Manufacturer Datasheets: This is the most reliable source.
- Online Forums: Tech forums are great for getting help from other enthusiasts.
- YouTube Tutorials: Many videos.
Conclusion: Mastering the Laptop WiFi Card Pinout
We hope this guide has demystified the world of laptop WiFi card pinouts. From understanding the basics to troubleshooting, we've explored the complexities of these critical components. Remember to approach this process with patience, care, and a healthy dose of curiosity. Happy tech-ing!
FAQs About Laptop WiFi Card Pinouts
What is the primary purpose of a WiFi card's pinout?
The pinout acts as a blueprint, showing how the pins on the WiFi card connect with other components in your laptop, which is essential for any repair or upgrade.
Is it safe to try changing the WiFi card on my own?
Changing a WiFi card can be done at home, but requires careful handling and knowledge. Always shut down the laptop and follow the correct safety procedures.
What do the antenna connectors on the WiFi card actually do?
The antenna connectors connect to the laptop's antennas, which are responsible for sending and receiving
WiFI Card vs USB WiFi Adapter Check out this comparison

By ADVANTI WiFI Card vs USB WiFi Adapter Check out this comparison by ADVANTI
How to remove and reattach WiFi antenna cables

By James Has Answers How to remove and reattach WiFi antenna cables by James Has Answers
How To Repair Laptop WiFi Card Laptop WiFi Card No Signal Repair

By Real Tech Academy How To Repair Laptop WiFi Card Laptop WiFi Card No Signal Repair by Real Tech Academy

Title: USB-C to Ethernet Connector Adapter for Wifi Internetusb adapterapple windowsmacbookmacnitesh
Channel: Mac Nitesh
USB-C to Ethernet Connector Adapter for Wifi Internetusb adapterapple windowsmacbookmacnitesh by Mac Nitesh
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
Laptop WiFi Card Pinout: The Ultimate Guide (With Pictures!)
Navigating the intricate world of laptop Wi-Fi cards can seem daunting. Understanding the pinout, that essential roadmap of connectivity, unlocks the ability to troubleshoot, upgrade, and often, breathe new life into your trusty machine. This guide provides a comprehensive deep dive into laptop Wi-Fi card pinouts, translating complex technical specifications into clear, actionable knowledge.
Deciphering the Importance of a WiFi Card Pinout
Before we delve into the specifics, let's clarify why a Wi-Fi card pinout is so crucial. This pin arrangement dictates how the card interfaces with your laptop's motherboard. It manages the flow of data, power, and communication signals. Knowing the pinout allows you to identify the function of each pin. This knowledge is essential for:
- Troubleshooting Connection Issues: Identifying which pins are responsible for specific functions enables precise diagnostics when Wi-Fi connectivity falters. A dropped signal or failure to detect a network often stems from a pin-related problem.
- Upgrading Your Wireless Card: If you’re considering a Wi-Fi card upgrade to 802.11ax or a faster version, understanding the pinout helps ensure compatibility with your laptop's existing hardware. Incorrect pin configurations could lead to significant problems.
- Card Replacement: When a Wi-Fi card must be replaced (due to damages), understanding the correct pinout helps you select a suitable replacement.
- Customization and Experimentation: Advanced users can use pinout information to explore the potential of their cards. This includes the possibility of creating custom antennas, or manipulating the card’s electrical behavior.
The Primary Connector Types: A Visual Overview
Laptop Wi-Fi cards haven't a single pinout standard. Instead, numerous connector types exist. The most common ones are:
- Mini PCI-e: This is among the more seasoned interfaces. It is commonly found in older laptops. It features a rectangular connector with 52 pins.
- M.2 (NGFF - Next Generation Form Factor): This is a more modern interface. It is more prevalent in newer laptops. M.2 cards come in different "keys" (A, B, E, M), determining their function and pin configuration. M.2 cards are slender and compact, specifically engineered for space-saving designs.
Mini PCI-e Pinout Breakdown
The Mini PCI-e (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, though less prevalent presently, remains significant, particularly for older laptops. It's a standardized connector. The following table provides a detailed explanation of each pin’s function.
| Pin Number | Signal Name | Function | | :--------- | :------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | 1 | 3.3V | Power Supply (3.3 Volts) | | 2 | 3.3V | Power Supply (3.3 Volts) | | 3 | GND | Ground | | 4 | GND | Ground | | 5 | CLKREQ# | Clock Request (Active Low) – Signals the need for a clock signal from the system. | | 6 | WAKE# | Wake-Up Request (Active Low) - Instructs the system to wake up from a sleep state. | | 7 | PERST# | PCI Express Reset (Active Low) – Resets the PCI Express interface. | | 8 | SMBCLK | System Management Bus Clock – Used for communication with the system's management controller. | | 9 | SMBDATA | System Management Bus Data – Carries data for communication with the system's management controller. | | 10 | GND | Ground | | 11 | REFCLK+ | Reference Clock Positive – PCI Express reference clock signals. | | 12 | REFCLK- | Reference Clock Negative – PCI Express reference clock signals. | | 13 | GND | Ground | | 14 | PERn0 | PCI Express Receive Data Lane 0 Negative | | 15 | PERp0 | PCI Express Receive Data Lane 0 Positive | | 16 | GND | Ground | | 17 | PETn0 | PCI Express Transmit Data Lane 0 Negative | | 18 | PETp0 | PCI Express Transmit Data Lane 0 Positive | | 19 | GND | Ground | | 20 | RESERVED | Reserved/No Connect | | 21 | GND | Ground | | 22 | +12V | Power Supply (12 Volts, not always used) | | 23 | +12V | Power Supply (12 Volts, not always used) | | 24 | GND | Ground | | 25 | GND | Ground | | 26 | UIMPWR | Universal Integrated Circuit Card Power (SIM card power, if applicable) | | 27 | UIMDATA | Universal Integrated Circuit Card Data – Data line for the SIM card, if applicable. | | 28 | UIMCLK | Universal Integrated Circuit Card Clock – Clock line for the SIM card, if applicable. | | 29 | UIMRESET | Universal Integrated Circuit Card Reset – Reset line for the SIM card, if applicable. | | 30 | GND | Ground | | 31 | UIMPRESENT | Universal Integrated Circuit Card Present – Indicates the presence of a SIM card, if applicable. | | 32 | UIMVPP | Universal Integrated Circuit Card VPP – SIM card power voltage (not always present), if applicable. | | 33 | GND | Ground | | 34 | LEDWWAN | Wireless Wide Area Network LED (if applicable) | | 35 | LEDWLAN | Wireless Local Area Network LED | | 36 | GND | Ground | | 37 | AUXP1 | Auxiliary Antenna Port 1 | | 38 | AUXN1 | Auxiliary Antenna Port 1 | | 39 | GND | Ground | | 40 | MAINP | Main Antenna Port | | 41 | MAINN | Main Antenna Port | | 42 | GND | Ground | | 43 | COLDP | Coaxial Cable Detection Positive (rarely used) | | 44 | COLDN | Coaxial Cable Detection Negative (rarely used) | | 45 | GND | Ground | | 46 | GND | Ground | | 47 | RESERVED | Reserved/No Connect | | 48 | RESERVED | Reserved/No Connect | | 49 | RESERVED | Reserved/No Connect | | 50 | +3.3V | Power Supply (3.3 Volts) | | 51 | +3.3V | Power Supply (3.3 Volts) | | 52 | GND | Ground |
The M.2 (NGFF): a Further Examination
M.2 is the modern standard, offering higher speeds and more features than its predecessors. The pinout varies based on the "key" of the M.2 card. The keys dictate what functions the card performs.
- Key A: Typically supports Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- Key B: Supports SATA or PCIe.
- Key E: Supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and WiGig.
- Key M: Primarily used for SSD storage, but also for high-speed PCIe devices.
- Key B+M: Supports both B and M keys.
The number of pins varies depending on the key. Some M.2 cards have 75 pins or more. Since the exact pinout depends on the key, one must refer to the specific datasheet for the Wi-Fi card to get accurate information. M.2 cards use significantly fewer pins than Mini PCI-e cards.
**(Note: Accurate pinout diagrams for specific M.2 cards are often found in the card's datasheet or technical documentation. Due to the wide variety of M.2 key configurations and card manufacturers, providing a generic pinout is not practical. Therefore, the specific pinout data for M.
