how to setup wifi on my laptop windows 10
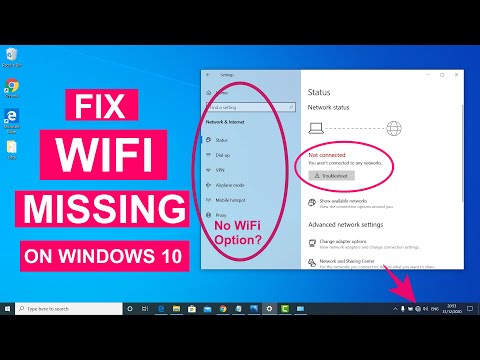
Title: Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
Channel: Sandeep Singh
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
how to connect wifi on the laptop windows 10, how to connect wifi on my hp laptop windows 10, how to connect wifi from phone to laptop windows 10, how to setup wifi on windows 10, how to find wifi in laptop windows 10
WiFi on Windows 10? Solved in 60 Seconds!
WiFi on Windows 10: Reclaim Your Connection in a Blink!
Ever stared at your Windows 10 screen, the WiFi icon stubbornly showing a disconnect? It’s incredibly frustrating. Don’t worry, though! Fixing that issue is often much quicker than brewing a cup of coffee. In fact, we might just get your internet humming in less time. Are you ready to troubleshoot?
The Dreaded WiFi Dropout: A Common Windows 10 Agony
Firstly, let us address the elephant in the room. WiFi problems plague Windows 10 users everywhere. It is incredibly prevalent. Suddenly losing your connection can disrupt everything. From important work tasks to streaming your favorite shows, the impact is large. Therefore, understanding how to swiftly address these issues is crucial. This knowledge will save you time, and certainly, considerable frustration.
Quick Fixes: Your WiFi Emergency Kit
Before diving into complex solutions, we should consider the simplest answers first. Sometimes, the answer is surprisingly obvious. Thus, try these initial steps before anything else.
The Classic Restart: Restarting your computer is the first step. It’s a standard solution for a reason. Furthermore, this can iron out unexpected glitches.
Check the Router: Ensure your router is functioning. Are all the lights blinking as they should? If not, restart the router. Unplug it for 30 seconds, then plug it back in.
Airplane Mode: Double-check that Airplane Mode is off. It’s the easiest mistake to make. Consequently, it often blocks your WiFi connection.
Physical Switch: Some laptops have a physical WiFi switch. Be sure it's in the "on" position.
Digging Deeper: Troubleshooting Advanced Options
Still no WiFi? Don't panic. Consequently, we can look at more advanced solutions. These steps are a little more involved. However, they usually resolve the problem.
Network Troubleshooter: Your Built-In Assistant
Windows 10 has a built-in network troubleshooter. It is your friend in these moments. Therefore, let's utilize it.
- Go to your Settings. You can find it by clicking the gear icon on the Start Menu.
- Click on "Network & Internet".
- Select "Status".
- Find "Network troubleshooter" and click it. Windows will attempt to diagnose and fix the problem.
Driver Drama: Updating Your Network Adapter
Sometimes, an outdated or corrupted driver is the culprit. As a result, updating the driver could be the remedy. Here's how:
- Right-click the Start button. Then, select "Device Manager."
- Expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Right-click your WiFi adapter.
- Select "Update driver". Choose “Search automatically for drivers”. Windows will then search for the latest version.
- If that doesn't work, choose "Browse my computer for drivers."
- Alternatively, uninstall your WiFi adapter. Then, restart your computer, and Windows should reinstall it automatically.
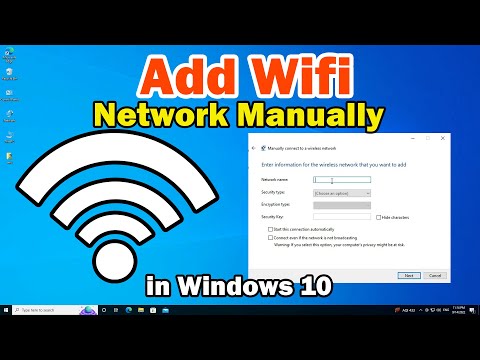
Hidden SSID? Don't Panic!
If your WiFi network is hidden, it won't automatically appear in the list. So, you'll need to add it manually.
- Click on the WiFi icon in the system tray.
- Select "Network settings."
- Choose "Manage Wi-Fi settings." You'll find an option to "Manually connect to a network."
- Enter your network name, security type, and password.
Advanced Tactics: The Last Resorts
These are often the more complex fixes. Try everything above before diving in.
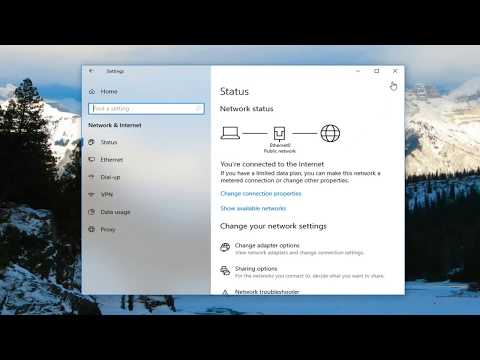
Network Reset: If all else fails, you can reset your network settings. However, be aware that this resets your network configuration.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Scroll down to "Network reset".
- Click "Reset now", and confirm.
Command Prompt Power: Flushing the DNS
Sometimes, your DNS cache can cause problems. Therefore, you can flush it using the Command Prompt.
- Type "cmd" into the Windows search bar.
- Right-click "Command Prompt" and select "Run as administrator".
- Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
ipconfig /flushdnsipconfig /registerdnsipconfig /releaseipconfig /renewnetsh winsock reset
- Restart your computer.
WiFi Revival: Success is Within Reach!
In conclusion, Windows 10 WiFi woes are annoying. They don’t have to be insurmountable, though. These steps should help you regain your connection. Furthermore, you should be back online in no time. Remember to try the simple solutions first. Consequently, you can often solve the issue quickly. If those fail, move on to the advanced options. Finally, if all else fails, consider contacting Microsoft support. Good luck. Enjoy your internet! Perhaps, you should bookmark this article for future reference.
Laptop to Printer Wireless: The SHOCKINGLY Easy Fix!WiFi on Windows 10? Solved in 60 Seconds!
Hey there, tech adventurers! Ever felt like your Windows 10 laptop is playing hide-and-seek with your Wi-Fi? One minute you’re surfing the web, the next, you’re staring at that dreaded “no internet” icon, feeling as disconnected as a hermit in a phone booth. We’ve all been there, right? It's like the internet suddenly vanishes into thin air, leaving you stranded. But what if I told you that getting your Wi-Fi back up and running on Windows 10 could be as quick as making a cup of coffee? Let’s dive in, shall we?
1. The Wi-Fi Woes: A Familiar Story
Think back to the last time your Wi-Fi decided to take a vacation. Were you in the middle of an important Zoom call? Finishing that crucial work document? Or, more importantly, were you about to bingewatch your favorite show? The frustration is real, the struggle is genuine. Windows 10, with its intricacies, can sometimes make you feel like you're deciphering ancient hieroglyphs just to get online. But fear not, because we’re here to simplify things!
2. Understanding the Culprit: Common Wi-Fi Problems
Before we whip out our virtual toolkits, let's understand the usual suspects. Sometimes it's as simple as accidentally hitting the airplane mode button (we’ve all done it!), or the Wi-Fi adapter got disabled somehow. Other times, drivers might be playing up, or the network itself might be having a bad day. It’s like a digital detective game, trying to sniff out the root cause.
3. The First Breath: Check the Basics!
Before you start tearing your hair out, let’s take a deep breath and check the obvious. Is the Wi-Fi switch on your laptop enabled? Is your router powered on and spewing out that sweet, sweet internet signal? It sounds basic, but you'd be surprised how often these humble checks save the day. It's like remembering to check for gas before you start driving – essential!
4. Airplane Mode: Your Silent Nemesis?
This one gets us all every now and then! Airplane mode – meant for, you know, flying – can be a sneaky culprit. Ensure it isn't enabled, as it will kill all your wireless connections. Just click the Wi-Fi icon in the bottom-right corner of your screen, and make sure Airplane mode is toggled off.
5. The Network Adapter: The Gatekeeper of Connectivity
Your network adapter is like the translator, converting your PC’s language to something your router understands. Sometimes, it just needs a nudge. To check its status:
- Right-click the Start button.
- Choose "Device Manager."
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Locate your Wi-Fi adapter (it’ll usually have “Wireless” in the name).
- Right-click it and select "Enable device" if it's grayed out.
6. Restarting the Adapter: A Digital Reset
If enabling it doesn't work, try the classic restart. Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter in Device Manager and choose "Disable device," then right-click again and select "Enable device." It’s like hitting the reset button on your brain.
7. The Troubleshooter: Windows' Secret Weapon
Windows 10 comes with a built-in troubleshooter, a digital Sherlock Holmes ready to investigate your Wi-Fi mysteries. To use it:
- Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray.
- Select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Let Windows do its thing. It’s usually pretty good at finding and fixing common issues.
8. Driver Updates: Keeping Things Fresh
Outdated drivers are like old tires on a racecar – they’ll slow you down. Make sure your Wi-Fi adapter drivers are up to date. In Device Manager (as described earlier):
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Select "Update driver."
- Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
Windows will search for the latest and greatest updates.
9. Router Reboot: The Digital Spring Cleaning
Sometimes, the problem isn’t with Windows 10, but with your router. It's the equivalent of getting a bad case of the blues. Reboot your router by unplugging it for about 30 seconds and then plugging it back in. This simple step often works wonders.
10. Forget and Reconnect: A Fresh Start
If you’ve tried everything else, try "forgetting" the network and reconnecting. This is the equivalent of a digital cleanse, wiping the slate clean:
- Click the Wi-Fi icon.
- Right-click on your network name.
- Choose "Forget."
- Then, reconnect and re-enter your password.
11. Check the Wi-Fi Channel:
Sometimes, the channels used by your router might be overcrowded. Check your router’s configuration to see if you can optimize the channel.
12. Network Reset: The Nuclear Option (Use with Caution!)
If all else fails, you can reset your network settings. This is like giving your computer a digital enema, which can sometimes solve deeper issues:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Scroll down and click "Network reset."
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
This will remove and reinstall all your network adapters, and set other network components back to their original settings.
13. Is Your Network Hiding? Check Visibility
Ensure your network isn’t hidden, if it is, connect to it again. Sometimes, networks can be configured to be hidden. This means their names won't simply pop up in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If you know your Wi-Fi network’s name, connect to it manually.
14. The Nuclear Option Part 2: Reinstall the Network Adapter
If a network reset doesn't suffice, then you may want to uninstall and then reinstall your network adapter. Find your Wi-Fi adapter in Device Manager (as discussed above). Right-click on it and select "Uninstall device." Restart your computer following this. When Windows starts up again automatically, the operating system should recognize the missing driver.
15. The 60-Second Wi-Fi Fix: A Quick Recap
Let's recap the crucial steps in a lightning-fast 60-second fix!
- Check Airplane Mode: Off? Good.
- Router Reboot: Unplug and plug back in.
- Troubleshooter Run: Let Windows work its magic.
- Driver Update: Ensure you have the latest.
- Forget and Reconnect: Start afresh.
Closing Thoughts: Back Online in a Flash!
So there you have it! Getting your Wi-Fi back up and running on Windows 10 doesn’t have to be a Herculean task. These steps, from the simple checks to slightly more involved troubleshooting, should get you back online in a jiffy. Remember, tech issues can sometimes be frustrating, but with a little patience and these quick wins, you can reclaim your digital life. Now go forth, and conquer the digital world!
Principal Keywords: Windows 10, Wi-Fi, Solve, Fix, Internet. SEO Headline: Wi-Fi on Windows 10: 60-Second Fix! Pathway: Windows-Wifi-Fix Meta Summary: Troubleshoot and fix Wi-Fi problems fast! This guide provides easy steps to solve Wi-Fi issues in Windows 10 within 60 seconds. Image Alt Text: Frustrated person looking at a computer with a 'no internet' sign.
FAQs: Your Wi-Fi Questions Answered!
Q1: Why does my Wi-Fi keep disconnecting on Windows 10?
A: This can be due to several factors: outdated drivers, router issues, network interference, or power-saving settings on your Wi-Fi adapter. Follow the steps outlined above to address these potential causes.
Q2: How do I know if my Wi-Fi adapter is the problem?
A: If other devices connect to the internet without issues, but your Windows 10 laptop is struggling, the Wi-Fi adapter is a likely culprit. Check in Device Manager to see if it’s enabled and if its drivers are up to date.
Q3: Should I update my Wi-Fi drivers, or is it safe to leave them as they are?
A: It is always a good idea to keep your Wi-Fi drivers up-to-date, as they can improve performance, stability, and security. Update drivers via Device Manager or automatically through Windows Update.
Q4: What can cause slow Wi-Fi speeds on my Windows 10 computer?
A: Slow speeds could be due to a crowded Wi-Fi channel, distance from the router, interference from other devices, or bandwidth limitations. If you use multiple devices, test and see. Try restarting your computer and your network router to see if this solves the problem.
**Q5: My Wi-Fi works on other devices, but not Windows 10; what should
Dell Inspiron i5: SHOCKING 2.4GHz WiFi ONLY? (Find Out Why!)How to Add Wireless Wifi Network Manually in Windows 10 PC or Laptop
By Discover You How to Add Wireless Wifi Network Manually in Windows 10 PC or Laptop by Discover You
How to Connect a Windows 10 Laptop PC to Wi-Fi Internet for beginners
By My Mate VINCE How to Connect a Windows 10 Laptop PC to Wi-Fi Internet for beginners by My Mate VINCE
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit

By Howtosolveit How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
Title: How to Create Wifi Hotspot in Windows 10 Tutorial
Channel: MDTechVideos
How to Create Wifi Hotspot in Windows 10 Tutorial by MDTechVideos
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
WiFi on Windows 10? Solved in 60 Seconds!
We understand your frustration. That flickering WiFi icon, the sudden disconnects, the sluggish loading times – it's enough to make anyone want to throw their laptop across the room. But before you resort to such drastic measures, take a deep breath. We're here to tell you that, in most cases, the solution to your Windows 10 WiFi woes is far simpler than you might imagine. Forget hours spent troubleshooting and countless browser tabs open with conflicting advice; we can indeed conquer these connectivity issues in a remarkably short timeframe.
Diagnosing the Problem: Pinpointing the Source of Your WiFi Woes
Before we dive into solutions, let’s acknowledge a crucial point: not all WiFi problems are created equal. A slow connection is fundamentally different from a complete lack of connectivity. The first step is always to identify the precise nature of the issue. Are you unable to connect to any WiFi network at all? Can you connect, but the internet is agonizingly slow? Do you experience intermittent disconnects? Understanding the specific symptom will guide us toward the most effective resolution, saving you valuable time.
The Quick Fix: Basic Troubleshooting for Immediate Connectivity
Let's begin with the simplest, most easily implemented actions. Often, the solution is deceptively straightforward. We'll examine these essential first steps:
Restart Your Computer and Router: This seemingly obvious step is often the cure for various ills. Think of it as a digital reset. Restarting your computer clears temporary files and processes, while restarting your router flushes its memory and re-establishes connections. Ensure your router is fully powered on, take a brief moment to turn it off and then back on, then restart your Windows 10 device. Patience is key; allow both devices sufficient time to fully reboot and reconnect.
Check Your WiFi Switch (Physical and Virtual): Laptops often have a physical WiFi switch, usually found on the side or front of the device. Ensure it is flipped to the "on" position. Furthermore, Windows 10 has a built-in software switch for WiFi. Navigate to the system tray in the bottom right corner of your screen, next to the time and date. Click on the network icon (it often resembles a series of bars). Make sure WiFi is enabled in the menu that appears.
Run the Network Troubleshooter: Windows 10 includes a built-in troubleshooter designed to diagnose and fix common network problems automatically. To access it, simply right-click on the network icon in your system tray and select "Troubleshoot problems." Follow the on-screen prompts. This tool can often identify and resolve common issues with your network adapter, such as driver problems or incorrect settings.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Diving Deeper into Solutions
If the basic steps fail to resolve the issue, let's delve into more advanced troubleshooting techniques. These methods are more involved but often provide definitive solutions to persistent connectivity problems.
Updating Your Network Adapter Driver: Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers are a common culprit behind WiFi issues. To update your driver, go to the Device Manager. You can find this by searching for "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar, or right-clicking on the Start button and selecting it from the menu. Expand the "Network adapters" section. Right-click on your WiFi adapter (it will usually have "Wireless" or "WiFi" in its name) and select "Update driver." Choose to search automatically for updated driver software. Windows will then search your device's manufacturer's website or its own driver repository for the latest version. If Windows can't find an update, you can manually download the driver from your computer manufacturer's website, such as Dell, HP, or Lenovo, depending on your device. Be sure to download the correct version for your specific model of laptop.
Resetting Your TCP/IP Stack and Winsock: Occasionally, the TCP/IP stack (the set of protocols that govern internet communication) or Winsock (Windows Sockets, which manages network connections) can become corrupted, leading to connection problems. To reset these, open Command Prompt as an administrator. You can search for "Command Prompt" in the Windows search bar, right-click on it, and select "Run as administrator." In the Command Prompt window, type the following commands, pressing Enter after each one:
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip reset
Then, restart your computer. This action resets the network settings to their default values.
Flushing Your DNS Cache: Your computer caches DNS information to speed up website loading times. However, this cache can sometimes become outdated and cause connection issues. To flush the DNS cache, open Command Prompt as an administrator and type the following command:
ipconfig /flushdns
Press Enter.
Modifying Power Management Settings for Your Network Adapter: Windows 10 can sometimes conserve power by selectively turning off your network adapter. This can lead to connectivity problems. To adjust these settings, go to Device Manager, as described above. Expand "Network adapters," right-click your WiFi adapter, and select "Properties." In the Properties window, go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that says, "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." Restart your computer after making this change.
Reinstalling Your Network Adapter: If all else fails, consider reinstalling your network adapter. In Device Manager, right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Uninstall device." Confirm the uninstallation. Then, restart your computer. Windows will automatically reinstall the network adapter.
Advanced Router-Related Troubleshooting: Checking your WiFi Router
The WiFi router is the gateway to your internet connection. WiFi problems are often related to router settings and configurations. Let's consider some key points:
Check Your Router's Firmware: Router firmware is the software that controls your router's operations. Outdated firmware can cause a wide range of issues, including WiFi disconnects. Access your router's administration panel by typing its IP address into your web browser (the address is usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but can be found in your router's documentation), enter the login credentials (usually "admin" for both username and password, though this is often customizable). Look for a "Firmware Update" or "Administration" section. Follow the instructions to check for and install any available firmware updates. This process often involves downloading a firmware file from the manufacturer's website and uploading it to your router.
Changing Your WiFi Channel: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. In crowded environments (such as apartments or office buildings) interference from other networks can cause connection problems. Log in to your router's administration panel (as described above). Look for a "Wireless Settings" or "WiFi Settings" section. Change the WiFi channel to a less crowded one. Most routers offer an option to automatically select the best channel; otherwise, experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended, as they do not overlap).
Router Placement and Interference: The physical location of your router can significantly impact WiFi performance. Make sure your router is placed in a central, open location, away from walls, metal objects, and electronic devices that can cause interference (e.g., microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices). Elevating your router can also improve signal coverage.
Check Your Router's Security Settings: Ensure your WiFi network is secured with a strong password. Using older security protocols, such as WEP, are significantly less secure than WPA2 or WPA3. In your router's settings, select WPA2 or WPA3 for the best security.
Network Adapter and Advanced Settings
Your network adapter has many configuration considerations beyond what we previously covered.
Adjusting Wireless Adapter Properties: In Device Manager, locate your WiFi adapter, right-click on it and select properties. Navigate to the Advanced tab. You'll find several configurable settings. Experiment with these settings to potentially improve connectivity and performance. Depending on your adapter, you might see options such as "802.11n/ac/ax Mode," which determines the highest WiFi standard your adapter supports, and "Transmit Power," which controls the strength of the signal. Note: it's important to write down the original settings before modifying them. Otherwise you can restore your settings.
Consider Power Saving Mode: Consider the power saving mode for the adapter. You can disable it to improve stability.
Preventative Measures to Minimize Future Issues:
The goal is not just to fix the problem but to prevent it from recurring. Employ these measures:
Regularly Update Your Drivers: Keep your network adapter drivers updated by regularly visiting the manufacturer's website or utilizing Windows Update.
Keep Windows 10 Updated: Install Windows 10 updates as soon as they become available. These updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can impact your network connectivity.
Invest in a High-Quality Router: A reliable router is the foundation of a stable WiFi network. Consider investing in a router from a reputable brand that supports the latest WiFi standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E).
Monitor Your Network's Performance: Regularly check your internet speed using online speed tests (e.g., Speedtest by Ookla) to monitor your connection's health. This will help you to identify any performance degradation.
By systematically applying these troubleshooting steps, you
