how to check wifi in laptop windows 7

Title: CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7
Channel: Rdn Channel
CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7 by Rdn Channel
how to find wifi in laptop windows 7, how to check wifi password in laptop windows 7, how to see wifi password in laptop windows 7, how to find wifi password in laptop windows 7, how to know wifi password in laptop windows 7, how to scan wifi qr code in laptop windows 7, how to check internet speed on laptop windows 7, how to find wifi mac address of laptop in windows 7, how to see saved wifi password on laptop windows 7, how to check wifi in windows 7
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW!
Windows 7 WiFi Woes: Conquering the Connectivity Chaos
Alright, let's be frank. Remember those days wrestling with your Windows 7 machine? Then you probably remember the Wi-Fi. It was a beast sometimes, wasn't it? That frustrating dance of dropped connections and endless troubleshooting. But fear not, because we're going to tackle this head-on together.
The Dreaded "Limited Connectivity" Curse
Do you recall that sinking feeling? The little yellow triangle. It screamed "Limited Connectivity." Suddenly, you were cut off from the digital world. This issue plagued many Windows 7 users. Several things could cause this frustrating message. First, the usual suspects: a weak signal or router problems. These are often easy to fix. Second, there are more insidious culprits at play. Drivers are a good place to look.
Unmasking the Culprits: Driver Dilemmas Uncovered
Drivers, those tiny software programs, are crucial. They are essential for your computer to communicate with your Wi-Fi adapter. Outdated or corrupted drivers are common villains. They caused many Windows 7 Wi-Fi headaches. You can often fix driver problems relatively quickly.
Here's How to Tackle It
First, let's check your drivers. Head to Device Manager. Find your network adapter. Then, right-click and select "Update driver software." Windows will search for a newer driver. It can also automatically install a fresh one. If that doesn't work, try manually downloading a driver. Visit your adapter manufacturer's website. Download the latest driver for your model. Next, install the new driver. Finally, restart your computer.
The Router's Role: A Signal Strength Saga
Your router is your Wi-Fi's central hub. It broadcasts the signal. Often, router issues cause connection problems. Is your router too far away? Obstructions like walls can weaken the signal. Position your router strategically. This ensures the best coverage. Also, check your router's settings. Sometimes, changing the wireless channel helps. This avoids interference from other networks.
Security Settings: Taming the Wireless Firewall
Security settings can also interfere. Some security software might block your connection. Check your firewall settings. Ensure that your Wi-Fi network is allowed. Additionally, review your router's security settings. Make sure they are set to WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. These offer better security.
Troubleshooting Tactics: Diagnostics and Deductions
So, what happens if the basics don't work? Then, it's time for some advanced troubleshooting. Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter. It’s a surprisingly effective tool. It will scan for common problems. Then, it will suggest solutions. You can access it by right-clicking on the network icon. After that, choose "Troubleshoot problems."
The IP Address Puzzle: Decoding Network Secrets
Sometimes, your computer isn't getting the right IP address. This causes connectivity issues. In the Command Prompt, you can release and renew your IP address. Type ipconfig /release, then press Enter. After that, type ipconfig /renew, and press Enter again. This resets your network configuration. It often resolves connection problems.
Power Management Prowess: Controlling Adapter Energy
Windows 7 has power-saving features. They might accidentally disable your Wi-Fi adapter. Go to Device Manager again. Find your network adapter. Right-click it, and select "Properties." Go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." That is a very useful trick.
The Ultimate Connection Checklist: Reclaiming Your Online Life
Let's summarize the key steps. First, update your drivers. Second, optimize your router position and configuration. Third, check your firewall settings. Then, run the network troubleshooter. Next, release and renew your IP address. Finally, adjust your power management settings. By following these steps, you can conquer your Wi-Fi woes.
Final Thoughts: Staying Connected in the Digital Age
Windows 7, though old, can still shine. It definitely has some quirks. Wi-Fi problems can be incredibly frustrating. But, when you follow these steps, you'll resolve them. After that, you'll be back online in no time. Stay connected, and keep exploring the digital world. Enjoy your faster, more reliable Wi-Fi experience!
Sony Vaio WiFi Nightmare? Solved! (Guaranteed Connection!)Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW!
Let’s be honest, remembering Windows 7 in 2024 feels a bit like dusting off a vintage sports car. You love it, it holds a special place in your heart (and maybe your garage!), but sometimes, getting it to actually work is a whole other story. And when we're talking about Windows 7 WiFi, it's often less "vroom vroom" and more "uh oh, no internet." So, if you’re still clinging to your trusty Windows 7 machine (no judgment here – I still have a soft spot for my old XP!), and you're wrestling with a WiFi connection that's more temperamental than a toddler at bedtime, then buckle up. We're diving headfirst into the world of Windows 7 WiFi woes and, more importantly, how to fix them.
1. The Unforgiving Truth: Is Your Windows 7 Still Secure? (And Why WiFi's Complicated)
Before we even think about troubleshooting your WiFi, we need to have a quick chat about security. Windows 7 reached its end of life a while back, meaning Microsoft no longer provides security updates. Think of it like this: your computer is a castle, and the drawbridge is down. Any passing digital bandit can stroll right in. This vulnerability drastically increases the risks you face online. So, while we’re fixing your WiFi, remember to consider the safety of your data. Using a reliable antivirus is paramount, and taking steps to secure your network, like using a strong password, is absolutely essential. Now, about that WiFi… It’s essentially a radio wave party, and sometimes Windows 7 just can’t hear the music.
2. The Early Signs: Recognizing the WiFi Woes
First things first: let's diagnose the problem. Is your WiFi icon showing a red X? A yellow warning triangle? Or is it just… absent altogether? These are crucial clues. Perhaps the icon shows a strong signal, but you still can't access the internet – a classic sign of an IP address conflict. Or, maybe you're stuck with "Limited Access," which feels like a digital slap in the face. Understanding what you're seeing is half the battle. We'll be diagnosing the underlying problem.
3. The Obvious First Steps: Restart, Then Restart Again!
Okay, I know, I know – it sounds cliché. But honestly, restarting your computer and your router really does fix things more often than you’d think. It's the digital equivalent of turning it off and on again. Think of your router as the conductor of your internet orchestra. Sometimes, the conductor has a brain freeze. Restarting clears the memory and gives everything a fresh start, often resolving temporary glitches.
- Restart your computer: The classic. Reboot your Windows 7 machine.
- Restart your router: Unplug your router from the power outlet, wait about 30 seconds, and plug it back in. This is like giving your internet a digital defibrillator!
- Restart your modem: The same process applies to your modem, which is the initial connection point to the internet (if you have one separately).
4. Digging Deeper: Checking Your Network Adapter
If restarting didn't do the trick, let's check your network adapter. This is the hardware responsible for connecting your computer to the WiFi.
- Open Device Manager: Click the Start menu, search for "Device Manager," and open it.
- Expand "Network adapters": Look for your WiFi adapter (it might have a name like "Wireless Network Adapter" or something similar).
- Check for issues: Is there a yellow exclamation mark or red X next to the adapter? That's a sign of trouble.
5. Driver Dilemma: Updating or Reinstalling Your Network Adapter
If you find an issue with your network adapter in Device Manager, the next step is usually dealing with the drivers. Think of drivers as the translator between your computer and the hardware. Outdated, corrupted, or missing drivers can wreak havoc.
- Update drivers: Right-click your WiFi adapter in Device Manager and choose "Update driver." Select "Search automatically for drivers."
- Reinstall drivers: If updating doesn't work, right-click the adapter, choose "Uninstall device." Then, restart your computer. Windows should try to reinstall the correct drivers automatically.
6. The Wireless Network Troubleshooter: Your Built-in Detective
Windows 7 actually has a built-in troubleshooter designed to help diagnose and fix network problems. Think of it as your digital detective.
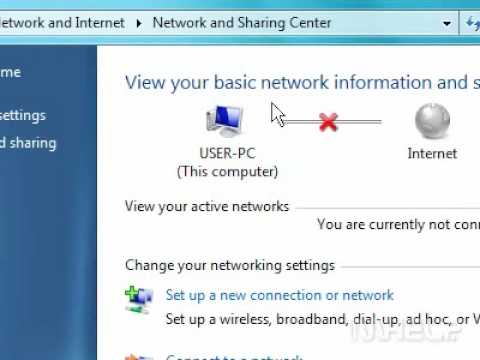
- Open Network and Sharing Center: Click the Start menu and search for "Network and Sharing Center."
- Click "Troubleshoot problems": In the Network and Sharing Center, look for the "Troubleshoot problems" link and click it.
- Follow the prompts: Select “Internet Connections” or “Troubleshoot network adapter” and let the troubleshooter do its thing.
7. IP Address Conflicts: The Digital Squatters
Sometimes, two devices on your network can have the same IP address, causing a "squatter's rights" situation. This leads to internet connectivity problems.
- Release and renew your IP address: Open the Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Start menu). Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter, then typeipconfig /renewand press Enter. This can often solve IP address conflicts.
8. Wireless Network Security: The Password Paradox
Is your password correct? Double-check the password you're entering. Make sure you're using the right capitalization and symbols. It seems basic, but it’s surprisingly common. You'd be surprised at how many times I've helped someone who just mistyped their WiFi password.
9. The Router's Rhythms: Channel Changes and Interference
Your router uses a specific "channel" to broadcast its WiFi signal. Neighboring routers can interfere with each other, causing slow speeds or dropped connections.
- Access your router's settings: You'll usually need to type your router's IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into a web browser and log in using your router's username and password. Look up your router's manual if you are not familiar with the process.
- Change the WiFi channel: Within your router's settings, look for the WiFi channel settings and try changing the channel. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally considered the least congested.
10. Firewall Fumbles: The Gatekeeper's Mistake
Sometimes, your firewall, which acts like a digital gatekeeper, can block your computer from accessing the internet.
- Temporarily disable your firewall: In rare instances, disabling your firewall temporarily (e.g., Windows Firewall or a third-party firewall) can help determine if it’s blocking your connection. Be careful when disabling your firewall, and remember to turn it back on once you've finished troubleshooting.
- Add an exception: If your firewall is the culprit, you can often add an exception in its settings to allow your computer to access the internet.
11. The Distance Debacle: Signal Strength and Physical Obstacles
WiFi signals, like whispers, weaken over distance and can be blocked by walls, furniture, and even microwaves.
- Move closer to the router: If possible, move your computer closer to your router to see if it improves the signal strength.
- Minimize obstructions: Ensure that there are few physical obstructions, like thick walls or large appliances, between your computer and the router.
12. Antenna Antics: External Adapters and Signal Boosters
For those facing persistent signal problems, particularly on older laptops, an external USB WiFi adapter or a signal booster might be the answer.
- Consider an external WiFi adapter: A USB WiFi adapter can often provide a stronger signal than the built-in adapter on your computer.
- Explore a WiFi signal booster: These devices amplify your WiFi signal, extending your reach, and improving connectivity.
13. The Wired Alternative: Is Ethernet Your Savior?
If you're in a pinch and can't get WiFi working, consider using an Ethernet cable to connect directly to your router. This is a surefire way to get online and troubleshoot your WiFi issues.
14. Router Firmware Fixes: The Digital Updates
Just like your computer, your router needs occasional updates, called firmware updates. Firmware updates often contain fixes for bugs and improve performance.
- Check for firmware updates: In your router's settings, look for a section to check for firmware updates. Follow the instructions to update your router's firmware.
15. Last Resort: The Nuclear Option (But Don't Panic!) - Resetting Your Router
If all else fails, you might consider resetting your router to its factory settings. This will erase all your custom settings, so make sure you know your internet provider's information.
- Locate the reset button: Most routers have a small reset button on the back.
- Press and hold the reset button: Use a paperclip or a similar object to press and hold the reset button for about 30 seconds.
- Configure your router: After the reset, you'll need to
Cara Mengaktifkan Koneksi Internet WiFi Di Windows 7

By MDTechVideos International Cara Mengaktifkan Koneksi Internet WiFi Di Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
Tidak terhubung tidak ada koneksi yang tersedia laptop windows 7

By IT Magics Tidak terhubung tidak ada koneksi yang tersedia laptop windows 7 by IT Magics

Title: Cara melihat kata sandi wifi pada Laptop windows 7
Channel: LAPTOP TUTORIAL
Cara melihat kata sandi wifi pada Laptop windows 7 by LAPTOP TUTORIAL
Working With Laptop
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solve It NOW!
The internet, a vast ocean of information and connection, has become as essential to our modern lives as the air we breathe. It's how we work, communicate, learn, and entertain ourselves. Yet, when that vital link falters, when the bars on our WiFi signal stubbornly refuse to budge, a digital frustration sets in. For those of us still navigating the familiar landscape of Windows 7, these wireless woes can be particularly vexing. This article is your lighthouse in the storm. We understand your frustration, and we’re here to guide you through the process of reclaiming your online freedom. Forget the endless searching and the vague advice; let's dive into concrete solutions to reignite your WiFi connection and banish the "Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare" once and for all.
Diagnosing the Dreaded Disconnect: Pinpointing the Problem
Before we can prescribe a cure, we need to understand the illness. A malfunctioning Wi-Fi connection in Windows 7 can manifest in several frustrating ways. Is your connection constantly dropping? Are you experiencing excruciatingly slow speeds? Or perhaps you can't even see your network in the list of available connections? Each scenario points to a different potential culprit, and precise diagnosis is crucial. Let’s break down the symptoms and the likely underlying causes.
- The "No Connection" Blues: If your computer flat-out refuses to detect your WiFi network, the problem could stem from disabled wireless functionality, incorrect network settings, or hardware malfunctions. Check your physical WiFi switch on your laptop, often located on the front or side. Ensure it is in the "on" position. Additionally, verify your wireless adapter is enabled in Device Manager (more on this later).
- The Intermittent Drop: Constant disconnections are often linked to driver conflicts, interference from other electronic devices (microwaves, cordless phones, and other WiFi networks), or a weak signal. The positioning of your router and the distance between your router and your computer play vital roles.
- The Sluggish Sufferer: Slow speeds can be caused by a range of factors, from outdated drivers and network congestion to a congested Wi-Fi channel and interference. Another possible explanation is the number of devices connected to your network, utilizing bandwidth simultaneously.
- The "Limited Connectivity" Conundrum: This frustrating message indicates that your computer can connect to the network, but it cannot access the internet. Common culprits include incorrect IP address settings, DNS issues, or problems with your router’s internet connection.
Unveiling the Device Manager: Your Windows 7 Command Center
Device Manager serves as the central hub for managing all hardware components in Windows 7, including your wireless network adapter. Accessing this tool is simple. Click the Start button, type "Device Manager" in the search box, and press Enter. Alternatively, right-click on "Computer" (either on your desktop or in the Start menu), select "Properties," and then click "Device Manager" in the left-hand panel.
Within Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" category. You should see your wireless network adapter listed (it might be labeled something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or "802.11n Wireless LAN Card"). Let’s explore the crucial actions you can take within Device Manager to resolve WiFi issues:
- Confirming Adapter Status: Look for any warning symbols (a yellow exclamation mark or a red "X") next to your wireless adapter. A yellow exclamation mark indicates a problem with the adapter, possibly due to a driver issue. A red "X" signifies that the adapter is disabled. If you see a yellow exclamation mark, right-click on the adapter and choose "Properties." The "General" tab will provide details about the issue. If the adapter is disabled, right-click it and select "Enable."
- Driver Updates: The Key to Compatibility: Outdated or corrupted drivers are a frequent source of WiFi problems. In Device Manager, right-click your wireless adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows 7 will search for and install the latest driver if available. If this automated process fails, you might need to obtain the driver from your computer manufacturer's website or the wireless adapter manufacturer's website. Locate the support or driver download section. Download the correct driver for your specific model of adapter and operating system (Windows 7, 32-bit or 64-bit). After downloading, run the installer to update the driver.
- Driver Rollback: Reversing the Changes: If a recent driver update caused the problem, you can roll back to a previous version. In Device Manager, right-click your wireless adapter, select "Properties," and then go to the "Driver" tab. If the "Roll Back Driver" button is enabled, click it to revert to the previous driver.
- Uninstalling and Reinstalling: In desperate cases, uninstalling and reinstalling the wireless adapter driver can resolve stubborn issues. Right-click the adapter in Device Manager and select "Uninstall." Restart your computer. Windows 7 should automatically attempt to reinstall the driver upon restart. If not, you can manually reinstall the driver using the downloaded setup file from the manufacturer's website.
Decoding Your Network Settings: The IP Address and Beyond
Incorrect network settings can prevent you from connecting to the internet. Let's examine the most common settings that need careful attention.
- IP Address Configuration: Your computer needs an IP address to communicate with your router and the internet. By default, most home networks use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which automatically assigns an IP address to your computer. However, sometimes you might need to configure these settings manually.
- Open the "Network and Sharing Center" by clicking the network icon in your system tray (near the clock) and selecting "Open Network and Sharing Center."
- Click "Change adapter settings" in the left-hand panel.
- Right-click your wireless network adapter and select "Properties."
- In the "Networking" tab, select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties."
- Ensure "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. If not, select these options and click "OK" twice.
- DNS Server Configuration: The Domain Name System (DNS) translates website addresses (like google.com) into IP addresses. Sometimes, your ISP's DNS servers can be slow or unreliable. You can try using public DNS servers like Google's (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare's (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) to improve your connection speed. In the same "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties" window, you can manually enter the DNS server addresses under "Use the following DNS server addresses."
Router Reboot: The Simple Yet Often Effective Solution
Before you delve into more complex troubleshooting steps, try the simplest solution: rebooting your router. This can often clear temporary glitches and refresh the connection. Unplug your router from the power outlet. Wait for at least 30 seconds (a minute is even better). Plug the router back in and wait for it to fully power up. Usually, this takes a few minutes. Then, try connecting to the WiFi again.
Channel Surfing: Optimizing Your Wireless Performance
WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. If your router is using the same channel as a neighboring network, you can experience interference, leading to slower speeds and dropped connections.
- Accessing Your Router's Configuration: You typically access your router's configuration by entering its IP address into a web browser. This address is usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but it can vary. Consult your router's documentation to determine the correct IP address. You'll also need your router's username and password (usually printed on the router or in its documentation).
- Finding the Wireless Channel Settings: Once logged into your router's configuration, look for the "Wireless," "WiFi," or "Wireless Settings" section. Within this section, you should find the option to change the wireless channel.
- Choosing the Optimal Channel: Routers typically offer a choice of channels, usually between 1 and 11 (for 2.4 GHz networks). The best practice is to choose a channel that is least congested. You can use a WiFi analyzer app on your smartphone or computer (there are many free options available) to scan for nearby WiFi networks and identify the least crowded channels. Also, channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally considered the best choices because they don't overlap with each other.
- Applying the Changes: After selecting a new channel, save the changes in your router's configuration. Your router will usually restart the wireless network. Reconnect your computer to the WiFi network and test your connection.
Hardware Considerations: Assessing the Physical Realm
Sometimes, the problem isn't software-based. It can be caused by hardware issues.
- Router Placement: Position your router in a central location, away from walls, obstructions, and electronic devices that can cause interference (microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices). Elevate the router to maximize its signal range.
- Distance and Obstructions: The distance between your computer and the router affects the signal strength, as do physical barriers like walls and furniture. If possible, move your computer closer to the router or clear
