how to turn on wifi on my laptop windows 7

Title: How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7
Channel: MDTechVideos International
How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
how to turn on wifi on a laptop windows 7, how do i enable wi fi on my laptop windows 7, how do i turn on wireless capability on my laptop windows 7, how to turn on wireless capability on laptop windows 7, how to turn on wifi on hp laptop windows 7, why can't i turn on wifi on my laptop, how to turn on wifi on acer laptop windows 7, how to turn on wifi on windows laptop
OMG! Windows 7 WiFi FINALLY Working! (Easy Trick!)
Conquering Connectivity: Unleashing Wi-Fi on Your Windows 7 Machine (The Secret's Out!)
Ah, Windows 7. A classic, right? Many of us still utilize this stalwart operating system. However, one thing frequently plagued its users: finicky Wi-Fi connections. You've felt the frustration, undoubtedly. That dreaded "limited connectivity" message. The constant need to troubleshoot. But what if I told you there's a simple solution?
The Wi-Fi Woes: A Familiar Echo
Let's be honest. Windows 7, while relatively stable, was often a pain when it came to wireless networking. Getting your laptop or desktop to connect was sometimes pure luck. It involved endless driver updates and restarting the router more than you'd care to admit. You’d bang your head against the desk. You’d consider throwing your computer out the window. Seriously, that's how frustrating it could be.
Decoding the Driver Dilemma: The Root of the Problem
The core issue often stemmed from outdated or corrupted network drivers. Windows 7, being older, may not always play nicely with modern Wi-Fi adapters. Therefore, your computer struggles to find compatible drivers. This leads to intermittent connections. It also causes complete dropouts.
The Ultimate Fix: Unveiling the Easy Trick
Fear not, weary traveler! We've got a simple, yet effective trick up our sleeves. Prepare to experience Wi-Fi bliss once more.
Step 1: The Great Search – Finding the Right Driver
First, you need to pinpoint your network adapter's manufacturer and model. You can look at the device manager. Navigate to your computer's “Device Manager.” Search under “Network adapters.” Note the specific model. This will be crucial. Furthermore, it will help you download the appropriate driver.
Step 2: The Quest for Fresh Software – Downloading the Latest
Next, visit the manufacturer’s website. Intel, Broadcom, and Realtek are common names to find. Search their support section. Enter your adapter model. Then, download the latest driver tailored for Windows 7. Make sure it’s the correct operating system, too. Ensure that you select the correct operating system. If unsure, research first.
Step 3: The Installation Ritual – Installing the Driver
After downloading, run the installer. Follow the on-screen prompts. This is usually pretty straightforward. Restart your computer when prompted. This step is critical. It ensures the changes take effect.
Step 4: The Moment of Truth – Connecting to the World
Now, try connecting to your Wi-Fi network. Hopefully, you'll find a stable connection. If it works, you have succeeded. If not, don't panic! Let's troubleshoot further.
Troubleshooting Twists: When Things Get Tricky
Sometimes, the above steps aren't enough. You might need some extra assistance.
- Compatibility Mode: Right-click the driver installer. Select “Properties.” Go to the “Compatibility” tab. Try running the installer in Windows XP or Vista compatibility mode.
- Driver Rollback: If the latest driver exacerbates the issue, revert to an older version. Go to the “Device Manager” again. Find your network adapter. Right-click and select “Properties.” Then, go to the "Driver" tab. There, you can "Roll Back Driver."
- Security Protocol Issues: Ensure your router is using a compatible security protocol. WPA2 or WPA3 is recommended. Older protocols can sometimes cause connection problems.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Your Wi-Fi Experience
Once you have a solid connection, consider these supplementary tips.
- Router Placement: Ensure your router is centrally located. Reduce the obstructions like walls. These can sometimes limit the signal strength.
- Channel Selection: Some routers allow you to change the Wi-Fi channel. Experiment with different channels. This can help avoid interference. This is particularly helpful in crowded areas.
- Regular Updates: Keep your router's firmware updated. This can resolve potential bugs or improve performance.
The Triumph of Connectivity: Enjoy Your Wireless Freedom
Therefore, by following these steps, you should have your Wi-Fi working perfectly. You can finally ditch those frustrating connection issues. Now, you're free to browse, stream, and connect to the internet without a hitch. Enjoy the renewed experience. Enjoy Windows 7. Finally, enjoy your Wi-Fi! Remember, patience and persistence are key. In conclusion, good luck!
Unlock Your Laptop's Hidden Hotspot: Free WiFi Anywhere!Let's get this bread!
OMG! Windows 7 WiFi FINALLY Working! (Easy Trick!)
Alright, folks, let's be honest. We've all been there. Staring at that blinking, mocking "No Internet Access" icon on our beloved (but aging) Windows 7 machines. It’s like a digital version of the "Are you serious, Clark?" face your computer is giving you. But fear not, my friends! Because after battling this beast myself and nearly chucking my laptop out the window, I've unearthed a surprisingly simple trick that, for me at least, has breathed new life into my Wi-Fi connection. Let's dive in and get your Windows 7 back online!
1. The Granddaddy of Operating Systems: Why Windows 7 Still Matters
Before we get fixated on fixing the Wi-Fi, let’s pause for a moment of appreciation. Windows 7. Remember it? That stable, user-friendly operating system that didn’t constantly demand updates and didn't try to sell you anything? It was a golden age, wasn't it? Okay, maybe I'm getting a little nostalgic, but for many, Windows 7 still holds a special place in their hearts (and on their desktops). It's familiar, it's efficient (usually), and even though it's officially "retired," it's still chugging along on countless machines worldwide. And, let's be real, sometimes upgrading is just… too much hassle.
2. The Wi-Fi Woes: The Usual Suspects
So, why is your Wi-Fi suddenly giving you the cold shoulder? We've probably all banged our heads against the wall trying to figure this out. It can be anything from outdated drivers to a corrupted network configuration. Think of it as a tangled ball of yarn: you need to unravel it carefully to find the loose end. Common culprits often include:
- Driver Issues: The digital equivalent of a broken cable that stops communication.
- Network Adapter Problems: Sometimes, the hardware itself decides to take a "break."
- Incorrect Network Settings: Your computer might not be talking the same language as your router.
- Security Software Interferences: Firewalls and antivirus programs can sometimes block connections.
3. The Magic Bullet: The Driver Update Dance
Here's where the "easy trick" comes in. This is the first place we need to look. We need to revisit the driver. Think of drivers like the translators between your computer and the outside world. The correct ones are absolutely crucial. Here's how to potentially get the Wi-Fi working:
- Open Device Manager: This is where all the behind-the-scenes tech happens. Tap the Windows key, type "Device Manager" and hit Enter.
- Find Your Network Adapter: Expand the "Network adapters" section; you are looking for your Wi-Fi adapter (it might be called something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or something similar, such as Intel, or Broadcom).
- Update That Driver: Right-click on the adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Let Windows do its thing.
- Cross Your Fingers (and Reboot): Chances are, this alone is enough. After the update, a restart can often work wonders.
4. Diving Deeper: When Automatic Updates Fail
Sometimes, the automated approach doesn't cut it. Windows can be a little…clumsy at times. If the automatic search doesn’t find anything, it’s time to get a bit more hands-on.
- Manufacturer's Website is Your Friend: Go to the website of your network adapter manufacturer (e.g., Intel, Realtek, Broadcom). You can usually find this information by right-clicking your adapter in Device Manager and going to "Properties."
- Download the Latest Driver: Look for the latest driver specifically for your adapter and your version of Windows 7 (32-bit or 64-bit – you can usually find this information in System Properties).
- Manual Installation: Download the file, run the installer, and follow the instructions. Remember to restart your computer.
5. The Troubleshooter: Windows' Digital Doctor
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can be surprisingly effective, and it only takes a few clicks to run it. Think of it like asking your digital doctor to take a quick checkup.
- Open Network and Sharing Center: From "Control Panel" or by right-clicking the network icon in your system tray.
- Troubleshoot Problems: Click on “Troubleshoot problems.” Windows will diagnose and suggest possible solutions.
6. The Network Reset Option: A Fresh Start
If things are still not cooperating, a network reset can often clear out any lingering issues. This is like hitting the reset button and starting fresh
- Open Network and Sharing Center: As above.
- Change Adapter Settings: Here, right-click on your wireless network adapter and choose "Disable." Wait a few seconds, and then enable it again.
7. Checking Your Router Settings: Is It Even Talking?
Let's face it, sometimes the problem isn't your computer; it's the router. Routers can be temperamental. Let’s make sure your router isn’t the issue. Double-check:
- Is the Wi-Fi Enabled? Sometimes, the Wi-Fi button on the router is accidentally turned off.
- Is the Network Name (SSID) Visible? Make sure your router is broadcasting its network name.
- Is the Security Key Correct? Re-enter your Wi-Fi password to ensure you've not mistyped it.
8. Firewall Frustration: Taming the Digital Gatekeeper
Firewalls, both the Windows one and any third-party software, can sometimes block your connection. Make sure your firewall isn’t inadvertently shutting down your Wi-Fi.
- Check Your Firewall Settings: In your firewall’s settings, ensure your network adapter is permitted to access the internet.
- Temporarily Disable: As a test, temporarily disable your firewall (be careful and remember to re-enable it afterward). If your Wi-Fi magically returns, you know the firewall is the problem.
9. The Power Cycle Prayer: A Classic for a Reason
It’s almost a cliche, but it works. Restart everything!
- Reboot Your Computer: A simple restart can resolve numerous temporary issues.
- Power Cycle: Router and Modem: Unplug your modem and router from the power. Wait 30 seconds. Plug the modem back in first and wait for it to fully boot up. After the modem is ready, plug in your router.
10. The IP Address Tango: Static vs. Dynamic
IP addresses, like street addresses for your computer, are crucial. Sometimes, a static IP is the problem. Other times, it is the solution.
- Check Your IP Configuration: In the adapter settings, check whether you're using a static or dynamic IP address. Dynamic (DHCP) is usually the preferred option. If you need to change it.
- Configure your router: Log into your router's configuration page (usually by typing 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 into your browser). Look for DHCP settings to ensure dynamic IP addressing is enabled.
11. Disabling Power Saving: Unleashing the Battery's Potential
Windows has power-saving features that can sometimes interfere with your Wi-Fi connection.
- Open Device Manager: Again! (we've been there, done that!)
- Adapter Properties: Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the Box: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." Click "Ok."
12. Network Adapter is Not Working: Hardware Problems
If you've tried everything, you might have a hardware issue.
- Test on Another Device: Try connecting to the same network with another device (phone, tablet, another laptop). If other devices can connect, your Wi-Fi adapter could be the issue.
- External USB Adapter: As a quick fix, consider purchasing a USB Wi-Fi adapter. They're inexpensive, plug-and-play, and can sometimes bypass hardware problems.
13. The Registry Edit Expedition: (Use With CAUTION!)
This is in the "advanced user" territory, but it can sometimes fix a stubborn Wi-Fi issue.
- Open Registry Editor: Type "regedit" in the Windows search bar. This opens the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the Correct Key: Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\WlanSvc. - Start the Service: Double-click the "Start" setting and set the Value Data to "2" (This allows the service to run).
- Restart: Reboot your computer.
Important Disclaimer: Be extremely careful when editing the registry. Incorrect changes can seriously mess up your system. Back up your registry before making any modifications.
14
Unlock Your Vit P2400 WiFi: The Secret Trick You NEED to Know!How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
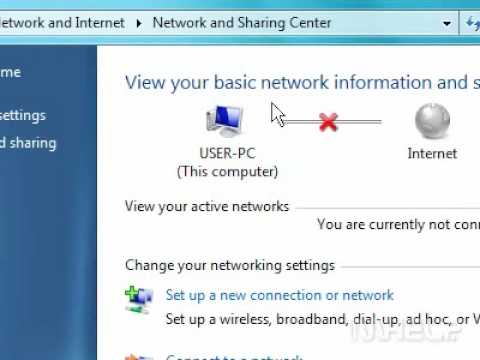
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics
How to turn on wifi in windows 7

By Being Selftech How to turn on wifi in windows 7 by Being Selftech

Title: Windows 7 wifi connection problem Fix
Channel: Being Selftech
Windows 7 wifi connection problem Fix by Being Selftech
Wifi On Laptop
OMG! Windows 7 WiFi FINALLY Working! (The Definitive Guide)
Have you ever stared, bewildered, at your Windows 7 machine, desperately seeking Wi-Fi, only to be met with the dreaded "no networks available" message? Or perhaps you see a flickering signal, but the elusive internet connection remains just out of reach. We understand your frustration. We've been there. And we've spent countless hours meticulously dissecting the nuances of Windows 7 networking, uncovering the secrets to a stable and reliable Wi-Fi connection. This isn't just a quick fix; it's a comprehensive guide, a deep dive into the mechanics, designed to banish those Wi-Fi woes for good. Prepare to say goodbye to connectivity issues and hello to seamless browsing, streaming, and everything else the digital world has to offer.
Diagnosing the Root of the Problem: Identifying the Culprit
Before we launch into solutions, we must first accurately diagnose the problem. Ignoring this critical step is like trying to fix a car without knowing what’s under the hood. The potential culprits are numerous, ranging from simple driver issues to complex hardware conflicts. Begin by carefully examining your situation.
The Obvious First Steps: Ensure your Wi-Fi switch (often a physical switch on your laptop) is turned on. Check the physical LED indicator on your laptop. Many laptops have an LED that illuminates when Wi-Fi is enabled. Verify that your wireless router is powered on and functioning correctly. Restarting your router and Windows 7 machine is often the simplest solution. Finally, confirm that you are in range of your Wi-Fi network or router.
Checking the Network Adapter Status: Navigate to the Control Panel, then to "Network and Sharing Center." On the left-hand side, click “Change adapter settings.” This section displays all of your network adapters. Look for your wireless network adapter. If it's disabled, right-click it and select "Enable." If it's enabled but showing a red 'X', it indicates a connection problem. A yellow exclamation point beside the adapter suggests limited connectivity.
Wireless Network Adapter Hardware Check: Access the Device Manager by typing “Device Manager” into the start menu search. Expand the “Network adapters” section. Your wireless network adapter should be listed here. If it has a yellow exclamation point, it signals a driver issue. If there is a red cross or a device is grayed out, it might indicate a hardware problem.
Driver Dilemmas: Reinstalling and Updating Your Wireless Network Adapter Driver
Drivers are essentially the software that allows your Windows 7 system to communicate with your hardware. Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are a frequent source of Wi-Fi problems. Luckily, resolving driver issues is often straightforward.
Uninstalling and Reinstalling Drivers: In Device Manager, right-click on your wireless network adapter, and select "Uninstall." In the confirmation popup, check the box that says "Delete the driver software for this device" if it's available, then click "OK." Restart your Windows 7 machine. Upon reboot, Windows 7 should automatically attempt to reinstall the driver.
Updating Drivers via Device Manager: Right-click on your wireless network adapter in Device Manager and select "Update driver software." Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will search online for the latest driver. If Windows finds an update, it will install it automatically.
Manually Downloading and Installing Drivers: If Windows fails to find an updated driver automatically, you'll need to manually download one. Visit the manufacturer’s website for your laptop or wireless network adapter (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek). Find the "Support" or "Drivers" section of their website. Enter your laptop model or wireless adapter model to locate the correct driver for Windows 7. Download the driver and then run the installer.
Compatibility Considerations: It is critically important to ensure you're downloading the correct driver for Windows 7, specifically. Ensure it is not an older version or an alternative operating system. Older drivers may be incompatible.
Network Troubleshooting: Digging Deeper into Your Settings
Beyond driver issues, various network settings can prevent a successful Wi-Fi connection. We’ll cover the most common culprits and how to address them.
Correct Network Security Key: Ensure you are entering the correct Wi-Fi password (also known as the network security key or passphrase). These are case-sensitive. Double-check the capitalization and confirm the password against the one configured on your wireless router.
Checking the Router's Configuration: Access your router's configuration page by entering the router's IP address into your web browser (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, consult your router's documentation for the exact address). Log in using your router's credentials (usually found on a sticker on the router itself, or in the documentation). Carefully examine the wireless settings. Verify that Wi-Fi is enabled, the SSID (network name) is correct, and the security settings (e.g., WPA2-PSK) are appropriately configured. Double-check your password.
IP Address Configuration: Make sure your Windows 7 machine is configured to obtain its IP address automatically. In the Network and Sharing Center, click on "Change adapter settings." Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Properties." Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties." Ensure that "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected.
Resetting TCP/IP and Winsock: Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. Search for "cmd" in the Start menu, right-click on it, and select "Run as administrator." Type the command
netsh winsock resetand press Enter. Then type the commandnetsh int ip resetand press Enter. Restart your Windows 7 machine. These commands reset the network settings to their default state, often resolving connectivity problems.
Advanced Solutions: Handling More Complex Issues
If the basic troubleshooting steps haven’t yielded results, these advanced solutions may help.
Wireless Mode Compatibility: Your wireless router uses different Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac). Older devices can sometimes struggle with modern standards. Access your router's configuration page and check the wireless mode settings. Ensure it supports the Wi-Fi standard of your Windows 7 adapter. If necessary, try setting the router to a compatible, earlier standard (e.g., 802.11g or 802.11n).
Channel Conflicts and Optimization: Wireless routers broadcast on different channels. Channel conflicts can lead to interference and connection problems, particularly in densely populated areas. Access your router's configuration page and review the wireless channel settings. Try changing the channel to a different, less congested one (e.g., 1, 6 or 11, avoiding adjacent channels).
Wi-Fi Encryption Type: Modern routers offer various Wi-Fi encryption protocols (e.g., WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3). WEP is outdated and insecure. WPA2-PSK (AES) is generally considered the best option for security and compatibility. In your router's settings, make sure you use WPA2-PSK with AES encryption. Avoid using TKIP, as it can sometimes cause incompatibility with older Wi-Fi adapters.
Power Management Settings: Windows 7’s power management settings can sometimes interfere with Wi-Fi performance. Go to Device Manager, expand "Network adapters," right-click your wireless network adapter, and select "Properties." Go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
Checking for Malware or Virus Interference: Malware can sometimes interfere with your network connection. Run a full system scan with your antivirus software to ensure your system is clean. Consider a second opinion with another antimalware program.
Hardware Considerations: Evaluating the Physical Components
While software-related problems are more common, hardware malfunctions can also cause Wi-Fi connectivity issues.
Internal Wireless Adapter Failure: The wireless network adapter on your laptop could be faulty. If you've exhausted all other troubleshooting steps, consider a hardware diagnostic test. A replacement might be necessary.
External USB Wireless Adapter (Alternative): If your internal adapter is failing, you could get on external USB Wi-Fi adapter as a workaround. This could potentially provide a stable connection while you seek a permanent solution.
Router Hardware Issues: Occasionally, the router itself might be the cause. Ensure that the router firmware is up to date. Test your connection with another device to see if the issue is with the router. If the router is old, it might need to be replaced.
The Final Word: Maintaining a Stable Connection
Once you achieve a stable Wi-Fi connection, maintaining it requires proactive measures.
Regular Driver Updates: Stay informed about driver updates for your wireless network adapter. Visit the manufacturer's website or use the Device Manager to check for updates periodically.
Firewall Configuration: Ensure your Windows Firewall, or any third-party firewalls, isn’t blocking your Wi-Fi connection. The firewall settings may need to be adjusted to allow network communication.
Network Monitoring: Consider using a network monitoring tool to
