can't enable wifi on laptop
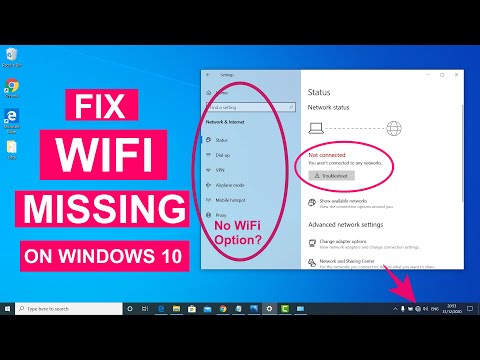
Title: Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
Channel: Sandeep Singh
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
can't enable wifi on laptop, how to enable wifi on laptop, how to enable wifi on laptop windows 10, how to enable wifi on laptop windows 11, how to enable wifi on laptop using keyboard, how to enable wifi on laptop windows 7, shortcut to enable wifi on laptop, can you disable wifi on laptop, how to enable wifi on laptop dell, how to enable wifi on laptop hp
WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop's Connection NOW!
Laptop WiFi Woes? Conquer Connectivity Chaos Today!
Ever felt the maddening frustration of a sputtering, sluggish Wi-Fi connection? You're not alone. That spinning wheel, the endless buffering – it's a modern-day digital torture. Fortunately, you can often reclaim your online sanity. Let's dive into how to fix your laptop’s WiFi.
Is Your WiFi Really the Culprit?
First, consider if the problem actually is your laptop. Before you start troubleshooting, rule out the obvious. Is every device in your home suffering the same slow speeds? If your phone, tablet, and smart TV are also struggling, the issue is likely with your internet service. Therefore, bypass your laptop for a moment. In that case, contact your internet provider. Perhaps they have a service outage. If only your machine is the problem, then read on.
Reboot, Refresh, Reconnect: A Simple First Aid Kit
Sometimes the simplest solutions prove the most effective. Start with the basics. Restart your laptop. Close all unnecessary applications before rebooting. Then switch off your router and modem. Wait at least thirty seconds. Turn your modem back on first. Allow it to fully boot up. Next, power up your router. Finally, let your router reconnect to the internet. This "power cycle" can often clear minor glitches. After it is back online, reconnect your laptop to the Wi-Fi network. Observe for any speed improvements.
Drivers: The Unsung Heroes (and Villains)
Outdated or corrupted network drivers can wreak havoc on your connection. Think of drivers as the translators between your laptop hardware and your operating system. To ensure smooth communication, you need to ensure they're up-to-date.
Here's how to update your network drivers (Windows is used here as an example, steps vary on other operating systems):
- Open Device Manager: Search for "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar. Then click to open it.
- Expand Network Adapters: Find and expand this section.
- Right-Click Your WiFi Adapter: Look for your wireless network adapter. It's likely named something like "Intel Wireless-AC" or "Qualcomm Atheros." Right-click on it.
- Update Driver: Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
- Restart: If Windows finds a new driver, install it, and restart your laptop.
Periodically updating drivers reduces your chance of problems. In addition, consider checking the manufacturer's website for the latest drivers.
Signal Strength Struggles: Location, Location, Location
Where you position your laptop relative to your router significantly impacts your connection quality. Walls, furniture, and other electronic devices can interfere with the signal. Concrete walls are particularly problematic. Move your laptop closer to the router. If possible, position your router in a central location. Try to elevate the router off the floor. Its signal then spreads more effectively.
Channel Congestion: Finding the Sweet Spot
Your Wi-Fi router broadcasts on a specific channel. If many other routers in your area use the same channel, it leads to congestion. Imagine multiple conversations happening simultaneously. The Wi-Fi is struggling to discern the signals. You can resolve this with a bit of effort.
- Access Your Router's Configuration: You'll typically access this by entering your router's IP address in your web browser. The IP address is often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Consult your router's manual if you're unsure.
- Log In: You will need your router's username and password. This information is also usually in the manual.
- Find the Wireless Settings: Look for a section labeled "Wireless," "Wi-Fi," or something similar.
- Change the Channel: Most routers allow you to select the Wi-Fi channel. You can often select "Auto." Some routers automatically choose the least congested channel. Otherwise, experiment with channels 1, 6, and 11. These channels are generally less crowded. Save your settings and restart your router. Now test if everything is working at a faster rate.
Security Protocols: Making the Right Choice.
Your router's security protocol also impacts performance. Older protocols (like WEP) are less secure and can sometimes slow down the connection. WPA2 or WPA3 is best. Check your router's settings. Then decide to upgrade if necessary. But first, make sure all devices support it. Therefore, choose the most secure protocol your devices support. This will boost security and may improve speed too.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Troubleshooting
If these steps don't resolve the problem, explore more advanced strategies. These may include:
- Checking for Interference: Microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and other electronics emit radio waves. This can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Keep your router away from these devices.
- Checking your Antivirus: In certain situations, your antivirus software may restrict your connection. Temporarily disable it. Then assess for problems.
- Router Firmware Update: Your router's firmware controls its functionality. Outdated firmware has performance bottlenecks. Therefore, see the manufacturers' websites for your router. Update the firmware, if necessary.
- Consider a Wi-Fi Extender: A Wi-Fi extender can expand your network's reach. It is useful for larger homes.
- Factory Reset (Use with Caution): A factory reset returns your router to its default settings. This is a last resort. Remember, you will have to reconfigure your settings.
When to Call in the Experts
If you've tried everything above, and you're still battling a sluggish connection, it's time to consider professional help. Contact your internet service provider or a computer repair technician. They can diagnose more complex hardware issues.
Ultimately, fixing your laptop's Wi-Fi connection often involves a bit of detective work. However, with these troubleshooting steps, you can likely banish those frustrating connection woes. You will be surfing the web at blazing speeds in no time. Enjoy your online experience!
Laptop WiFi Signal Nightmare? This Antenna & Booster Fixes It!WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop's Connection NOW!
Let's be honest, we've all been there. You're in the middle of something – a crucial work presentation, a thrilling online game, or even just trying to binge-watch your favorite show – and bam! The dreaded WiFi symbol with the little exclamation point appears. It's the digital equivalent of your car breaking down in the middle of nowhere. A WiFi nightmare. But fear not, fellow internet travelers! We're here to dissect this connectivity conundrum and get your laptop back online faster than you can say "buffered."
1. The Unholy Trinity: Understanding the Root of Your WiFi Woes
Before we dive into the fixes, we need to understand what's causing your laptop's internet agony. Think of your internet connection as a complex ecosystem. There are three main players, and if one of them is failing, the whole system collapses. The "Unholy Trinity" consists of:
- Your Laptop: This is your portal, the gateway to the digital world. If it's the problem, your journey is cut short.
- Your Router: The central hub, directing traffic and broadcasting the WiFi signal. It's the traffic controller of your home network.
- Your Internet Service Provider (ISP): The ultimate provider of the information highway. They're the ones feeding you the data.
Troubleshooting starts by figuring out which of these three is at fault. We'll go through diagnostics for each, starting with the most common culprit: your laptop.
2. Is It Really the WiFi? Double-Checking the Obvious
Sometimes, the simplest solution is the best. Before we start a deep dive, let's quickly rule out the obvious.
- Airplane Mode: Are you accidentally in Airplane Mode? It's happened to the best of us. Check your system tray (usually at the bottom right of your screen) for this symbol.
- WiFi Toggle: Is WiFi actually turned on? There's usually a simple on/off switch, maybe a function key (Fn + a key with a WiFi icon) or a physical toggle switch on the side of the laptop.
- Network Connection: Check if you're connected to your home network. Click the WiFi icon in your system tray to see available networks. Are you connected to the right one? Is the password correct?
- Restarting your laptop: The most straightforward fix is a simple restart. It’s like hitting a reset button. Sometimes, a fresh boot clears up all the issues.
3. Laptop First Aid: Diagnosing and Fixing Connection Issues
If the simple checks didn’t work, it's time to investigate your laptop's internal systems. Think of it like performing a quick check-up on your digital patient.
- Driver Detective: Outdated or corrupt drivers are the internet equivalent of a clogged artery. Here's what you do:
- Go to your Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar – or right-click your start button).
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Find your WiFi adapter (it'll likely have "Wireless" in the name).
- Right-click it and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
- If that doesn't do the trick, you may need to manually download the latest driver from your laptop manufacturer's website.
- Network Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in troubleshooter designed specifically for network issues. It's like having a digital doctor on call.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Click "Network troubleshooter." Let it run and see if it can identify and fix any problems.
- Flush the DNS: Over time, your computer accumulates a cache of DNS (Domain Name System) information, which helps it translate website addresses into IP addresses. Sometimes, this cache can get corrupted, causing connection problems.
- Open Command Prompt (search for it in the Windows search bar).
- Type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter. - Restart your computer.
4. Router Rescue: Checking Your Home's Traffic Control Center
If your laptop seems fine, the problem might be with your router. Think of it as the central traffic controller and ensure it's working correctly.
- The Power Cycle: This is the digital equivalent of "turning it off and on again." Unplug your router and modem, wait 30 seconds, plug the modem back in, wait for it to fully boot up, then plug the router back in. This simple act can often resolve minor glitches.
- Router Placement: Is your router hidden away in a closet? Or behind a huge metal object? Location, location, location! For the best signal, place your router in a central, open location. Avoid walls, metal objects, and other sources of interference.
- Checking the Lights: The lights on your router tell a story. Look for indicators of internet connectivity, WiFi signal strength, and device activity. If you spot any unusual patterns, consult your router's manual.
- Router Firmware: Just like your phone, your router has firmware that may need updating. Check your router's administration page (usually reached by typing the router's IP address in a web browser) for firmware updates.
5. ISP Interference?: When the Infrastructure Fails
Sometimes, the problem isn't your laptop or your router. It could be an issue with your Internet Service Provider(ISP).
- Check for Outages: Visit your ISP's website or use their customer service app to check for any reported outages in your area. This is the ultimate external factor.
- Slow Speed Tests: Run a speed test (search for "speed test" in Google) to see if your internet speeds are significantly below your advertised speeds. If so, contact your ISP.
- Contact Customer Service: When all else fails, it's time to reach out to your ISP's customer service. Explain the problems you're experiencing, and be prepared to answer troubleshooting questions. They might be able to help through remote diagnostics.
6. Signal Boosters and Mesh Networks: Expanding Your WiFi Reach
If you have dead zones in your home (places where the WiFi signal is weak or nonexistent), consider these options:
- WiFi Extenders: These devices pick up your existing WiFi signal and rebroadcast it, extending its range. It's like adding a megaphone to your router.
- Mesh Networks: Mesh networks use multiple access points to create a seamless WiFi coverage throughout your home. They are generally more sophisticated than extenders and provide better performance, roaming and signal strength.
7. Security First: Protecting Your WiFi Network
A secure network is a happy network. Here’s how to make sure your WiFi is not an open buffet:
- Strong Password: Use a strong, unique password for your WiFi network. Avoid easily guessed passwords.
- WPA3 Encryption: Make sure your router uses the latest WPA3 encryption protocol (if your devices support it). This is the digital equivalent of sturdy locks.
- Guest Network: Set up a guest network for visitors. This isolates their devices from your primary network, protecting your data.
8. Troubleshooting for Different Operating Systems
While our focus has mostly been on Windows, other operating systems can experience issues. Here’s some tips.
- Mac: macOS usually has reliable wireless connectivity. However, if there are problems, check the system preferences. Ensure WiFi is on, and attempt to reconnect to the network. Clear the DNS Cache.
- Chromebook and other Linux based devices: These are less prone to advanced configuration problems, but checking connectivity and troubleshooting basics can always help.
9. Avoiding Interference: The Silent Killers of WiFi
Even when everything is running smoothly, external factors can interfere with your WiFi signal.
- Microwaves and Other Appliances: These are notorious WiFi interferer's. Try moving your router away from them.
- Bluetooth Devices: Bluetooth devices can also cause interference. Disable them if they are not needed.
- Other Wireless Networks: If you live in an apartment building or densely populated area, your WiFi signal might be competing with other networks. Using a WiFi analyzer app can help you find a less crowded channel.
10. Optimizing Your Router Settings: Fine-Tuning for Performance
Beyond the basics, you can often optimize your router's settings for better performance.
- Channel Selection: Your router broadcasts on a specific channel. Some channels are less congested than others. Try using a WiFi analyzer to find the best channel for your situation.
- QoS (Quality of Service): This setting allows you to prioritize certain types of traffic, such as video streaming or online gaming.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Some routers allow you to adjust how bandwidth is allocated to each device.
11. Rebooting Your Digital Life: When to Consider a Factory Reset
If you've exhausted all other options, a factory reset might be necessary. This will return your router or laptop to its original settings.
- Caution: A factory reset wipes all custom settings, so proceed with care. Back up any important data first.
- Router Reset: Usually, there is a reset button on the back of your router. Use a paperclip to hold it for several seconds.
- Laptop Reset: You can perform
How to Turn on Wifi on Window 10 in Laptop Wifi Not Turning on Problem Solved Wifi Turned Off
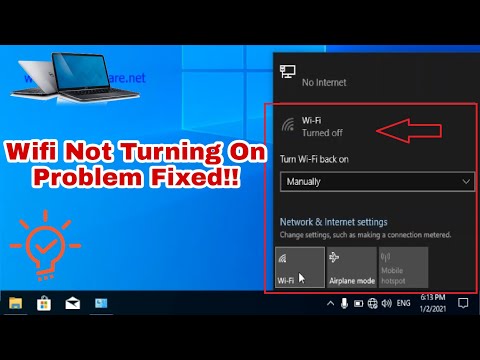
By Zeeshan Awan How to Turn on Wifi on Window 10 in Laptop Wifi Not Turning on Problem Solved Wifi Turned Off by Zeeshan Awan
4 cara mengatasi laptop tidak bisa terhubung ke wifi can't connect to this network pada windows 10

By Domminic Komputer 4 cara mengatasi laptop tidak bisa terhubung ke wifi can't connect to this network pada windows 10 by Domminic Komputer
How to Fix Missing Network Adapters on Windows Enable WiFi Network Adapter from BIOS Settings
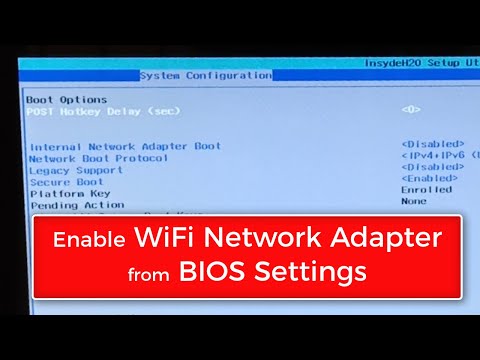
By WebbyFan How to Fix Missing Network Adapters on Windows Enable WiFi Network Adapter from BIOS Settings by WebbyFan

Title: How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit
Channel: Howtosolveit
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop's Connection NOW!
We've all been there. The spinning wheel of doom. The pixelated video call. The agonizing wait for a webpage to load. A sluggish Wi-Fi connection on your laptop can transform a productive work session into a frustrating ordeal. But before you hurl your laptop across the room, let’s explore the common culprits behind these connectivity calamities and, more importantly, how to conquer them. We'll dive deep into the various solutions, providing actionable steps to banish the buffering blues and reclaim your digital life.
Diagnosing the WiFi Demons: Identifying the Root Cause
Pinpointing the source of your laptop's Wi-Fi woes is the crucial first step. A systematic approach is key. Before you begin, make sure your other devices are working correctly by testing their Internet performance. Is your phone, tablet, or another computer experiencing the same issues? If yes, the problem likely resides with your internet service provider (ISP) or your router. However, if your laptop is the lone sufferer, then the focus shifts to resolving a problem specific to the laptop itself.
First, take a close look at the network icon in your system tray (usually in the bottom-right corner of your screen on Windows or the top-right on macOS). What does it show? A full signal strength with no internet access? A weak signal? Or no signal at all? This initial observation offers a critical data point. A weak signal suggests distance from the router or physical obstructions interfering with the signal. No signal implies either a disabled Wi-Fi adapter, problems with the router, or an outright failure.
Consider the physical location of your laptop. Are you far from the router? Are there walls, metal objects, or other electronic devices between your laptop and the router? These can significantly degrade the Wi-Fi signal. Try moving your laptop closer to the router or in a more open area. Observe the results. This simple experiment can often reveal a problem with the physical environment.
Think about the time of day. Are you experiencing slow speeds during peak hours when everyone else in your household is online? Overloaded bandwidth could be the issue. ISPs sometimes experience congestion, especially during evenings and weekends. Checking your internet speed on a speed test website (like Speedtest.net) during different times of the day can help you ascertain this.
Finally, review your recent actions. Did you install any new software or hardware recently? Some programs can interfere with network functionality, and new hardware, such as a docking station, might be at fault.
The Software Arsenal: Tuning Up Your Laptop’s Network Settings
Once you have a grasp of the potential causes, let's move to software-based troubleshooting. This is where many problems can be resolved with a few clicks.
1. The Restart Remedy: This is the digital equivalent of a physical reset. Reboot your laptop. Then, restart your router. A simple restart can clear temporary glitches that might be causing connection issues. Allow your router ample time to fully initialize after restarting before attempting to connect your laptop.
2. Driver Dilemmas: Outdated or corrupted network drivers can be a frequent cause of connectivity problems. To resolve this, navigate to your laptop's Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Expand the "Network adapters" section. Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (the name will vary depending on your laptop, but it usually contains "Wi-Fi" or "Wireless"). Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Let the system find and install any available updates. Alternatively, you can manually download the latest drivers from the manufacturer's website for your specific laptop model.
3. Network Troubleshooter: Windows and macOS both offer built-in network troubleshooters designed to identify and fix common problems. In Windows, search for "Network troubleshooter" in the search bar and run the utility. In macOS, go to System Preferences > Network, select your Wi-Fi connection, and click "Assistant" to run the diagnostic tool.
4. Forget and Reconnect: Sometimes, your laptop's stored network settings become corrupted. Delete your network profile, effectively "forgetting" the network, and then reconnect. On Windows, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi, click "Manage known networks," select your network, and choose "Forget." On macOS, go to System Preferences > Network, select Wi-Fi, and click "Advanced." Select your network and click the minus (-) button to delete it. Then, reconnect and enter the password.
5. IP Configuration Inspection: Incorrect IP address settings can prevent your laptop from connecting to the internet. Open the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS). Type ipconfig (Windows) or ifconfig (macOS) and press Enter. Examine the output. Do you have a valid IP address and default gateway? If not, try renewing your IP address. In the Command Prompt, type ipconfig /release followed by ipconfig /renew.
6. The DNS Directive: Your laptop uses DNS servers to translate website names (like google.com) into IP addresses (like 142.250.185.142). Sometimes, the default DNS servers provided by your ISP can be slow or unreliable. Consider changing them to more reliable public DNS servers, like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1). You can change the DNS settings in your network adapter properties (Windows) or in the Advanced settings for Wi-Fi (macOS).
Hardware Hacks: Enhancing Your Wireless Signal Strength
If software solutions fail, the problem could be related to your laptop’s hardware or the router.
1. Router Relocation and Optimization: The physical location of your router matters. Position it in a central, open location within your home, away from walls, metal objects, and other electronic devices that can cause interference. Elevate it if possible. Ensure the router's antennas are positioned correctly. Experiment with rotating them to see if the signal improves.
2. Router Firmware Updates: Router firmware is the underlying software that controls your router's functionality. Like any other software, it needs occasional updates. Outdated firmware can cause performance and security issues. Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing its IP address into a web browser – check your router's manual for the default address and login credentials) and check for available firmware updates.
3. Channel Congestion Combat: Wireless routers broadcast their signals on different channels. In crowded areas, multiple routers can interfere with each other, creating slow speeds. Access your router's configuration page and experiment with changing the Wi-Fi channel. Most routers offer an "auto" setting that can select the best channel dynamically, but it’s worth manually selecting different channels to find the one with the least interference.
4. Wireless Standard Verification: Ensure your router and laptop support the latest Wi-Fi standards (like 802.11ac or 802.11ax, also known as Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6, respectively). Older standards can be significantly slower. Check your laptop's specifications and your router's documentation. If your router and laptop support a newer standard but aren't using it, check your router's settings to ensure it's enabled.
5. Access Point Consideration: For larger homes or offices, a single router might not provide adequate coverage. Consider adding a wireless access point or a mesh Wi-Fi system to extend your network's reach. These devices can be placed throughout your home to provide a stronger, more consistent signal.
6. Antenna Augmentation: If your laptop has an internal antenna, you might be able to purchase an external antenna to boost its signal strength. However, this depends on your laptop model. Some laptops have external antenna ports. Others do not.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques:
If you've exhausted the above steps, consider the following more-advanced troubleshooting techniques.
1. Network Reset (Windows): Windows offers a network reset option that reverts all network settings to their default values. This can resolve persistent configuration issues. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced network settings and select "Network reset." Be aware that you will need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi networks and re-enter passwords after resetting your network settings.
2. Malware and Virus Scan: Malware can sometimes interfere with network functionality. Run a full scan using a reputable antivirus or anti-malware program.
3. Factory Reset (Last Resort): As a last resort, consider resetting your laptop to its factory settings. This will erase all data on your hard drive, so make sure to back up your important files before proceeding. This can often resolve persistent software conflicts that are causing network problems.
Preventative Measures: Keeping Your Connection Strong
Once you’ve fixed your Wi-Fi connection, consider these preventative measures to maintain optimal performance:
Regular Driver Updates: Periodically check for and install the latest network drivers for your laptop.
Router Monitoring: Regularly check your router’s configuration page for firmware updates and monitor its performance.
Network Security: Secure your Wi-Fi network with a strong password to prevent unauthorized access and potential bandwidth hogging.
Bandwidth Management: If you have multiple devices connected to your network, be mindful of bandwidth consumption. Avoid large downloads or streaming high-definition videos simultaneously on multiple devices.
Optimized Placement: Ensure your router is placed in an optimal location to provide maximum coverage.
By systematically applying these troubleshooting steps, you should be able to
