how to install wifi on laptop windows xp
Title: How to connect Windows XP to your wireless network
Channel: NetComm
How to connect Windows XP to your wireless network by NetComm
how to connect wifi in dell laptop windows xp, does windows xp support wifi, can windows xp connect to wifi
XP Wifi Nightmare Solved! (Windows XP Wireless Setup)
Windows XP Wifi Woes Vanquished: Conquer Your Wireless Setup!
Remember the days of dial-up? They seem positively ancient now! The internet is now a necessity, not a luxury. However, even with blazing-fast broadband, frustration can strike. That feeling arises when your Windows XP machine stubbornly refuses to connect to Wi-Fi. But fear not! Together, we'll navigate this digital labyrinth. Therefore, prepare to banish those connection headaches!
The Phantom of the Wireless: Identifying Your XP's Enemy
First, let’s identify the culprit. Does your XP machine even detect your wireless network? If it doesn’t, you're facing a fundamental problem. It could be a hardware issue. For instance, is the wireless card enabled? Check the physical switch on your laptop. Moreover, make sure the wireless adapter is correctly installed in Device Manager. In Device Manager, look for any yellow exclamation marks. These signify driver problems.
Decoding the Driver Dilemma: Your Wireless Wingman
Drivers often hold the key. Think of them as software interpreters. Specifically, they translate communication between your hardware and the operating system. Outdated or corrupted drivers can lead to Wi-Fi failure. Consequently, updating your drivers is often the first step.
Here’s how:
- Navigate to Device Manager (Start -> Run ->
devmgmt.msc). - Expand “Network adapters.”
- Locate your wireless adapter (it might be labeled something like “Wireless Network Adapter”).
- Right-click on the adapter and select "Update driver."
- Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
If Windows can't find updated drivers, you'll have to look online. Visit the manufacturer's website for your wireless adapter. Download the latest drivers. Therefore, install them manually. After installation, restart your computer. The Wi-Fi should spring to life!
SSID Secrets: Connecting to Your Wireless Fortress
Assuming the drivers are sorted, we shift focus to your network settings. Specifically, the Service Set Identifier (SSID). The SSID is merely your network's name. It’s what you see when your computer searches for available Wi-Fi networks. Ensure you're selecting the correct SSID. In case you share your network with others. Verify your password is accurate. Case sensitivity matters!
Encryption Enigmas: The Wireless Security Maze
Security protocols are important. They protect your precious data. Windows XP supports various Wi-Fi security protocols. However, older protocols like WEP are now considered weak. Therefore, it is essential to configure your router with WPA2 or WPA3. These are more secure. Make sure your XP machine also supports the chosen security protocol. Sometimes, you need to adjust your router settings. It’s a good idea to check your router’s documentation.
The IP Address Puzzle: Static or Dynamic?
Your computer requires an IP address to converse on the network. Typically, you'll use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This means your router automatically assigns an IP address. However, in some cases, a static IP address is needed.
To check your IP address settings:
- Open Network Connections (Start -> Control Panel -> Network Connections).
- Right-click your wireless connection.
- Select “Properties.”
- Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” or “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)."
- Click “Properties.”
Ensure “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” are selected. However, if you have a static IP, ensure the information is inputted correctly.
Firewall Follies: The Security Sentinel
Windows Firewall can sometimes cause connection problems. Consequently, it might be blocking your Wi-Fi connection. Temporarily disable the firewall to see if it’s the issue. Then, to allow the connection, you may need to configure exceptions. But, remember to reactivate the firewall after testing.
Troubleshooting Tactics: The Final Frontier
Still no luck? Don't despair! Here are a few more troubleshooting steps:
- Restart Everything: Restart your computer, router, and modem. It sounds simple, but it often works!
- Check the Router Channel: Sometimes, interference can disrupt Wi-Fi. Try changing your router's wireless channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended).
- Reinstall the Wireless Adapter: If all else fails, uninstall and then reinstall your wireless adapter. This will refresh the connection.
Victory Achieved: Embracing the Wireless World!
By systematically working through these steps, you should conquer your Windows XP Wi-Fi woes. Therefore, celebrate your newfound connectivity! You can finally enjoy the internet again. Remember to stay patient and persistent. Moreover, if you still have issues, consider seeking professional help. With a little effort, you can overcome any tech challenge!
HP Laptop WiFi Adapter: Where's the Hidden Hotspot?!XP Wifi Nightmare Solved! (Windows XP Wireless Setup)
Ah, Windows XP. That nostalgic operating system, a relic of a bygone internet era. We all have a soft spot for it, don't we? It was the gateway to the digital world for many of us, a time when dial-up tones were the soundtrack to our online adventures. But let's be honest, getting Wi-Fi working on good ol' XP? That could be a genuine headache, a digital Everest! The "XP Wifi Nightmare" as we lovingly, or perhaps not so lovingly, call it. Fear not, fellow digital pioneers! We’re cracking the code and making that aged hardware sing and, specifically, connect to the internet.
1. The Ghosts of Networks Past: Why XP Wi-Fi Can Be Tricky
Think of it like this: XP is a vintage car. Beautiful, charming, but definitely not built for the autobahn of modern Wi-Fi. The security protocols, the driver updates…oh, the driver updates! They’re like finding the right vintage engine for a classic car – sometimes, it takes a bit of elbow grease. The older protocols, like WEP, are about as secure as a paper door in a hurricane. Modern routers, with their WPA2/WPA3 security, often aren’t backward compatible. This incompatibility alone can be the root cause of the XP wifi nightmare.
We’re also talking about hardware. Old laptops and Wi-Fi adapters weren't exactly designed with the latest and greatest in mind. They often lack the processing power or compatibility to handle advanced encryption methods, leading to a frustrating lack of connectivity. But don't despair! We’ll navigate these murky waters, and soon you'll be browsing the web like it's 2003 all over again.
2. Before You Leap: What You'll Need to Tame the Wi-Fi Beast
Before we dive in, let's gather our supplies. This isn't a full-blown expedition, but it's smarter to be prepared.
- Your Windows XP Machine: Obviously! Make sure it's powered on and ready to go.
- A Wi-Fi Adapter: This is the crucial piece of equipment. If your laptop has an internal Wi-Fi card (most do), great! If not, you'll need a USB Wi-Fi adapter. Make sure it's compatible with Windows XP. You can usually find this information on the adapter's packaging or manufacturer's website.
- Your Router's Information: Jot down your router's SSID (network name) and Wi-Fi password. This will be essential for the setup process. Also, note the security type (WPA, WPA2, WEP).
- Drivers (Potentially): This is where things get interesting. Older Wi-Fi cards may require drivers, which are essentially software instructions. Have the drivers readily available. You might find them on a driver CD that came with your adapter or on the manufacturer's website. Or, if you're lucky, Windows XP might have them already.
- Patience (and a cup of coffee!): This is the most important ingredient! Sometimes, things go smoothly; other times, you might need a moment (or two) to troubleshoot.
3. Unearthing the Drivers: The Gatekeepers to Connection
Think of drivers as the translators for your Wi-Fi adapter. Without the right drivers, your XP machine simply won’t “speak” the language of Wi-Fi.
- Automatic Driver Installation: This works if your Wi-Fi adapter is plug-and-play, which is basically a USB adapter that easily installs itself. When you plug it in, XP might automatically detect and install the necessary drivers. Keep your fingers crossed for this one!
- Installing Drivers from a CD/DVD: If you have a driver CD/DVD, insert it, and follow the on-screen instructions. This is usually pretty straightforward.
- Downloading Drivers from the Internet: If you don't have a CD, you’ll need to obtain the drivers from the internet. This is the trickier route and requires another network connection. (This assumes you are trying to connect a laptop with no existing wi-fi!) Search for the manufacturer's website and download the XP drivers for your specific Wi-Fi adapter model. Transfer them to your XP machine using a USB drive or any other method that works.
- Dealing with Driver Issues: If you’re struggling to install the drivers, make sure you’re downloading the correct drivers for your specific Wi-Fi adapter and architecture (either 32-bit or 64-bit). Restarting your computer after driver installation is always a good idea.
4. Setting Up Your Wi-Fi Connection: The Configuration Capers
Once you've sorted out the drivers, the next step is configuring the Wi-Fi connection. This where you, the wizard, weave digital magic.
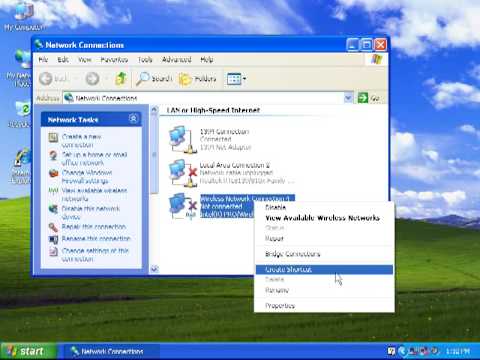
- Opening the Wireless Network Configuration: Click the network icon in the system tray (usually in the bottom-right corner of your screen). It's a little computer icon with a couple of bars. If you don't see it, you might need to enable your wireless card.
- Scanning for Networks: In the Wireless Network Connection window, select "View Wireless Networks". XP will then scan for available Wi-Fi networks.
- Choosing Your Network & Entering the Password: Select your network's name (SSID) from the list. Often, it will display the name of your router. If you have a strong password (you do, right?), you'll be prompted to enter it.
- The Security Dance: If your router uses WPA/WPA2 encryption, you'll select that option. If this connection proves unsuccessful, you may also need to consider the older, weaker WEP security. (More on this later, it comes with a health warning!)
- Troubleshooting Connection Problems: If you're unable to connect, double-check your password. Make sure the caps lock key isn't on. Also inspect your security settings on your router.
5. Playing With Security: The WEP/WPA/WPA2 Dilemma
Let's talk about security, the guardian of your precious data.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): This is the grandpa of Wi-Fi security. It's like a rusty lock on the front door – better than nothing, but easily bypassed. If your router only supports WEP, then you're in for some trouble – and you should seriously consider upgrading your router, or at a minimum, using a virtual private network (VPN) on your XP machine.
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): A step up from WEP, but still not the best. It offers better encryption.
- WPA2: The current industry's standard; this is a big jump in security. Your router should ideally support this.
- WPA3 (if available): The latest and greatest, even more secure. Unfortunately, XP generally doesn’t support this fully.
- The Bottom Line: For the best security, configure your router to use WPA2 (or, if you really must, WPA). If your XP machine cannot connect with these methods, you might need to consider the risk of using WEP. Don't forget to enable firewall on your XP machine!
6. The IP Address Assignment: Static vs. Dynamic
Think of an IP address as your computer's digital street address.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): This is the most common and easiest method. Your router automatically assigns an IP address to your XP machine. It's like having a delivery company assign your street address. It's usually set up by default.
- Static IP Address: You manually assign a specific IP address. You probably won't need this; it's more for advanced network setups.
If you're having connection problems, check if your network is trying to use a Static IP address automatically when you are on default (DHCP).
7. Troubleshooting Tips: When Things Get Sticky
Even the best of us face setbacks. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- No Network Found: Double-check your router's configuration and make sure it's broadcasting its SSID. Restart both your XP machine and your router.
- Incorrect Password: It's amazing how often this is the problem. Retype your password carefully, paying attention to capitalization.
- Driver Conflicts: Try uninstalling and reinstalling your Wi-Fi adapter drivers.
- Security Protocol Mismatch: Ensure your XP machine and router are using compatible security protocols (e.g., WPA2).
- Firewall Issues: Windows XP's built-in firewall may be blocking your connection. Temporarily disable it to test, but remember to re-enable it afterward.
- Antivirus Interference: Occasionally, your antivirus program can interfere with your network connection. Temporarily disable it if you suspect this is the issue.
- Check Your Cable Connections: If you’re connecting via Ethernet cable, make sure it is plugged in, at both your computer and to the router.
8. Advanced configurations: The Hidden Depths
For the truly tech-savvy, let's peek behind the curtain.
- Manual IP Configuration: If you need a static IP address, you'll find the
How To Fix Wifi Not Working In Windows XP Tutorial

By MDTechVideos How To Fix Wifi Not Working In Windows XP Tutorial by MDTechVideos
How to Connect to the Internet in Windows XP PC

By How-To Guide How to Connect to the Internet in Windows XP PC by How-To Guide

Title: Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011
Channel: inprez id
Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011 by inprez id
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
XP WiFi Nightmare Solved! (Windows XP Wireless Setup)
Staring at a flickering cursor on a Windows XP machine, wrestling with the phantom menace of wireless configuration? Don't despair. The digital ghosts of old-school operating systems can be exorcised, and a stable, secure WiFi connection is within your grasp. This guide cuts through the jargon and offers a clear path to connecting your faithful XP device to the modern wireless world. Prepare to banish the "limited connectivity" demons and reclaim your digital freedom.
Understanding the Wireless Landscape: Before You Begin
Before diving into the configuration, it's crucial to understand the basics. Windows XP's wireless support, while functional, is a relic of an earlier era. Security protocols, drivers, and network standards have evolved significantly since its heyday. Therefore, establishing a seamless connection often requires a carefully considered approach.
- Your Hardware: Ensure your computer has a wireless adapter. Most laptops from the XP era had built-in adapters. For desktops, you'll likely have a PCI or USB wireless adapter. Note the adapter's model number; you might need it for driver downloads.
- Your Router: Modern routers typically support various wireless standards (802.11 b/g/n/ac/ax). XP generally supports 802.11b and 802.11g, though a compatible adapter may enable support of 802.11n connections.
- Security Considerations: WPA/WPA2 encryption are essential. If your router is using the outdated WEP encryption, upgrade your router's firmware or consider replacing the device for the safest connection. WEP is easily cracked, leaving your network vulnerable.
- Driver Dependency: Legacy operating systems like XP heavily rely on the correct drivers for hardware functionality. Having the right driver is critical.
Driver Procurement: The Gateway to Connectivity
The correct driver is the cornerstone of a successful Wi-Fi setup. Finding the correct drivers can seem like a real hunt, but here’s how to navigate this potentially complex process.
Identify Your Wireless Adapter: Locate your wireless adapter. On a laptop, this information may be listed on a sticker or the manufacturer's label. For a desktop, look for the adapter's model number. If you're unsure, open the Device Manager (right-click "My Computer," then select "Manage," and click "Device Manager"). Expand the "Network adapters" section to find your adapter. If you see yellow exclamation points, you are most likely missing a driver or have a driver issue.
Manufacturer's Website: Visit the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek). Search for drivers specifically for your adapter's model number and Windows XP. Avoid generic driver downloads, as they may not be compatible.
Download and Install: Download the correct driver and run the installer. If a prompt arises, follow the on-screen instructions. Restart your computer after installation, if prompted.
Alternative Search Methods: If you're having trouble finding the drivers on the manufacturer's website, try the following:
- PC Manufacturer's Support Page: Check the support page of the computer manufacturer (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo). They often provide drivers specific to your model.
- Driver Databases: Explore reputable driver download sites (e.g., DriverGuide, DriverMax), but be cautious. Always scan downloaded files for viruses before installing them.
WEP and WPA Security: Keeping Your Network Secure
Security is paramount. The security of your wireless network is more critical than ever. Older security protocols are no longer fit for use. If your router is currently using WEP, immediately upgrade to the more secure WPA/WPA2.
Access Router Configuration: Access your router's configuration settings. Usually, you can do this by typing your router's IP address in a web browser (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Refer to your router's manual if you don't know the address or login credentials.
Locate Wireless Security Settings:
- Find the wireless security settings within your router's configuration. This section is typically labeled "Wireless Security", "Security," or something similar.
- If WEP is currently set, switch to WPA2-PSK (AES). It's the recommended option for optimal security and compatibility.
Set a Strong Password:
- Choose a strong, unique password for your wireless network. Remember, passwords should be at least 12 characters. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Make sure to select the same security type (WPA2-PSK) and password on your Windows XP machine.
Apply and Reboot: Save the changes to the router's configuration and restart your router. The router's restart is essential, and it will make sure that any changes you have made take effect.
Configuring the Wireless Connection in Windows XP
With your drivers installed and your network secured, it’s time to configure the wireless connection within Windows XP.
Open Wireless Network Connection Settings: Right-click the wireless network icon in the system tray (near the clock). This icon may look like small bars or a computer screen with a wireless signal. If it's not present, your adapter might not be properly installed or enabled. You can also access these settings through the Network Connections window from the Control Panel.
View Available Wireless Networks: Windows XP will scan for available wireless networks in range. You should see a list, including your network name (SSID).
Connect and Enter Security Key:
- Select your network from the list.
- If your network is secured with WPA2, you will be prompted to enter your network's security key (password). Enter the key precisely. Case matters.
Network Keys:
- XP will then attempt to connect to the network. If the security key has been typed correctly, XP should complete the connection.
- If it can't connect, ensure that you entered the security key correctly. Also, be sure that your router is broadcasting (SSID).
Enable Windows Wireless Zero Configuration:
- XP utilizes the Windows Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) service to manage wireless connections. Ensure the service is running.
- To verify, go to Start -> Run and type
services.mscand press Enter. - Locate the “Wireless Zero Configuration” service in the list. Make sure it is running. If it is not running, right-click the service and select "Start." Set the startup type to "Automatic."
Troubleshooting Common Wireless Issues
Even with the proper setup, you might encounter obstacles. Here's a troubleshooting guide to help you overcome them.
Limited or No Connectivity: If you connect to the network but have limited or no internet access:
- Check Router Connection: Confirm that your router has an active internet connection.
- IP Address: Double-check that your computer is receiving an IP address from the router.
- DNS Settings: Ensure your DNS settings are correct (often, automatic settings work best).
- Firewall: Disable your firewall temporarily to see if it blocks the internet connection. If this resolves the issue, configure your firewall to allow internet traffic.
Cannot See Your Network:
- SSID Broadcast: Make sure your router is broadcasting its SSID (network name). Some routers have this feature disabled by default.
- Router Distance: Ensure you are within your router's range.
- Hidden Network: If your network is hidden, you must manually enter the SSID and security key.
Connection Drops:
- Driver Updates: Update your wireless adapter's drivers to the latest version.
- Router Interference: Reduce interference by moving your computer or router away from devices that emit radio waves (microwaves, cordless phones).
- Signal Strength: Improve signal strength by repositioning your router or wireless adapter.
Security Key Issues:
- Case Sensitivity: Remember that the security key (password) is case-sensitive. Re-enter the key, paying close attention to capitalization.
- Router Settings Verification: Double-check that the security settings on your computer match those of your router (e.g., WPA2-PSK, same password).
- Router Firmware Updates: Upgrade your router's firmware, which can resolve compatibility and security issues.
Optimizing Performance and Security Long-Term
Once you have a stable connection, consider these steps to maximize performance and security.
Regular Driver Updates: Update your wireless adapter’s drivers regularly. Driver updates often include important security patches and performance improvements.
Firewall Protection: Enable a firewall on your Windows XP machine. Windows XP includes a built-in firewall, though it's less advanced than modern solutions. Or, install a third-party firewall for enhanced protection.
Antivirus Software: Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software. Antivirus software is essential to shield your XP machine from malware and viruses.
Password Security: Change your wireless network password regularly.

