laptop not showing wifi networks windows 10
Title: Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
Channel: Sandeep Singh
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
laptop not showing wifi networks windows 10, laptop not detecting wifi network windows 10, hp laptop not showing wifi connection windows 10, hp laptop not finding wifi network windows 10, lenovo laptop not detecting wireless network windows 10, laptop no wifi networks found windows 10, laptop no internet connection windows 10, windows 10 laptop not showing any wifi networks, laptop is not showing wifi networks, laptop windows 10 wifi not showing
WiFi Vanished! Fix Your Windows 10 Laptop NOW!
WiFi Woes? Your Windows 10 Laptop's Secret SOS
Ever felt the digital world slip away, leaving you adrift in a sea of buffering circles and disconnected dreams? It's a frustrating experience, especially when your trusty Windows 10 laptop suddenly refuses to play nice with your WiFi. Don't panic! While the situation might seem dire, hope isn't lost. In fact, we’ll guide you through some solutions to get you back online.
The Vanishing Act: Unraveling the Mystery
First things first, acknowledge the problem. Notice that your WiFi icon has mysteriously vanished. Or perhaps, it’s present but stubbornly refusing to connect. This digital disappearing act can stem from several culprits. These range from drivers needing a kickstart to your router throwing a temper tantrum. So relax; let's dive in.
Step 1: The Basics – A Quick Diagnostic Check
Before you launch into a full-blown troubleshooting frenzy, let's cover the basics. Firstly, make sure your WiFi switch, often located on the side or front of your laptop, is enabled. Secondly, double-check your router. Is it powered on? Are other devices connected? Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. In this case, it's a good place to start!
Step 2: The Driver Detective – Hunting Down the Culprit
Drivers are the unsung heroes of your laptop's functionality, including WiFi. Consider them the translators between your hardware and operating system. If a driver is outdated, corrupted, or missing, your WiFi connection will suffer. To investigate this, right-click the Start button (the Windows logo). Then, select "Device Manager" from the menu. A new window will open, unveiling a list of all the hardware on your laptop.
Focus on "Network adapters." Expand this section. You should see your WiFi adapter listed here. It might have a yellow exclamation mark or a downward-pointing arrow if there's a problem. If you see either of these, it means there's a driver issue. So, right-click your WiFi adapter. Choose to "Update driver". The system will prompt you to search automatically for updated drivers. Let Windows handle this.
Step 3: Resetting - A Digital Restart
Sometimes, a simple reset is all that's needed to coax your connection back to life. This involves restarting your network adapter. Go back into Device Manager, find your WiFi adapter, right-click it, and choose "Disable device." Wait a few seconds, and then right-click it again, selecting "Enable device." This often jumpstarts the connection.
Step 4: Network Troubleshooter – Your Digital Lifesaver
Windows 10 includes a built-in network troubleshooter. It's a fantastic tool. It can often identify and fix common connectivity problems automatically. To access it, type "troubleshoot" into your Windows search bar. Then, click "Troubleshoot settings". Select "Network Adapter" from the list. Click "Run the troubleshooter." Follow the on-screen prompts. It might suggest fixes.
Step 5: Router Reboot – Giving Technology a Break
Your router, the gateway to the internet, also needs a breather occasionally. Therefore, a reboot might be the key to resolving your WiFi issues. Unplug your router. Wait at least thirty seconds, giving it enough time to fully reset. Then, plug it back in. Allow it to power up completely before attempting to reconnect your laptop.
Step 6: Network Settings – Fine-Tuning Your Connection
Network settings can cause connection problems. Ensure your network profile is set correctly. Go to Settings (press the Windows key + "I"). Then, navigate to "Network & Internet." Select "WiFi." Click on "Manage known networks." Click on your network name, then "Properties." Verify if your network profile is set to "Private." This can affect how your laptop connects.
Step 7: The Last Resort – Reinstalling the Driver
If none of the above steps resolve your issue, you may need to reinstall your WiFi adapter driver. Go back to Device Manager. Right-click the adapter. This time, choose “Uninstall device.” A dialog box will appear. Make sure you check the box to “Delete the driver software.” Then, restart your laptop. Windows will automatically try to reinstall a driver. If not, you may need to visit your laptop manufacturer's website and download the latest driver. Download the correct version for your specific laptop model and Windows 10 version.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Troubleshooting
If the above troubleshooting steps fall short, consider these more advanced options. For example, you can reset your network settings. This will remove and reconfigure your network adapters. Resetting can sometimes resolve persistent issues. Also, consider checking for Windows Updates. Microsoft often releases updates that include new drivers or bug fixes.
Staying Connected: Preventing Future WiFi Woes
Once you've regained your WiFi connection, preventing future problems is key. Here are some proactive steps. First, keep your drivers updated. Regularly check for updates through Device Manager or your manufacturer's website. Second, ensure your router firmware is up to date. Manufacturers often release firmware updates. This enhances performance and security. Finally, keep your laptop clean of malware. Malware can interfere with your network connection.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Digital Life
Losing your WiFi can be frustrating. However, armed with these troubleshooting steps, you are well-equipped to handle the situation. Remember to be patient. Try each solution methodically. In most cases, you'll have your WiFi back up and running in no time. Now, reconnect and enjoy the online world!
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? Solved! (Secret Trick Inside!)WiFi Vanished! Fix Your Windows 10 Laptop NOW!
Oh, the dreaded moment! You reach for your laptop, ready to dive into the digital world, and… poof… no WiFi. The icon in the corner, that little symbol of connectivity, is either missing, crossed out, or stubbornly refusing to cooperate. Panic might start to bubble, because let’s be honest, we’re all reliant on the internet these days. From checking emails to streaming our favorite shows, a missing WiFi connection can feel like a digital desert. But take a deep breath, because we've all been there, and more importantly, we can usually fix it! This guide will walk you through the most common culprits behind your vanished WiFi and how to get back online in a flash. Consider this your personal WiFi rescue mission!
1. The "Are You Sure You're Even Connected?" Check-Up!
Before we start pulling apart your digital engine, let's begin with the simplest checks. It’s like making sure your car has gas before assuming the engine's dead.
- Is your WiFi router switched on? Sounds silly, I know, but trust me, it happens! Check the power light. It might be flashing, indicating a problem, or just plain off, meaning it's time to flip the switch or check the power cord.
- Is your router broadcasting a signal? Most routers have indicator lights. Look for the one labeled "WiFi" or a similar symbol. If it's off or flashing in an unusual pattern, the problem might be with your router, not your laptop.
- Is your internet service working? Grab your phone (that’s likely on WiFi) and try to browse the internet. If your phone also can't connect, the issue is likely with your internet service provider (ISP).
Why these checks are crucial: Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the ones we overlook while desperately troubleshooting complex issues. Think of it as shaking the snow globe before dismantling your digital empire.
2. The Airplane Mode Fiasco: Don't Let a Little Plane Ground You!
Okay, so the router is humming, the internet is flowing, but still no WiFi? This is when we check the most common culprits. First on our list: Airplane Mode! This is a setting designed to disable all wireless connections, which means your WiFi is immediately switched off. It’s easy to accidentally trigger, especially if you’re using a keyboard shortcut.
- How to Check: Look for the Airplane Mode icon (a plane) in your system tray (the bottom right corner of your screen). If it's active (usually highlighted), click it to disable Airplane Mode. Alternatively, press the Windows key + A to open the Action Center, where you'll find the Airplane Mode toggle.
Think of Airplane Mode as a silent assassin – easily activated, often forgotten, and capable of causing major connectivity woes.
3. Taming the Troublesome WiFi Adapter: Your Laptop's Wireless Bodyguard
Your WiFi adapter is the hardware inside your laptop that actually receives the WiFi signal. It’s the digital equivalent of your laptop's antenna. If there's a problem with your adapter, you're not going to be surfing the web.
- Checking the Adapter's Status: Right-click the Start button and choose "Device Manager" or search for it in the Windows search bar. Look for "Network adapters." Expand this section. You should see your WiFi adapter listed (it'll often include the word "Wireless" or "WiFi").
- What to Look For:
- A disabled adapter: If the adapter has a down arrow symbol, it's disabled. Right-click it and choose "Enable device."
- An adapter with an error: A yellow exclamation mark indicates a problem. Right-click and select "Update driver" to install the latest driver.
- An adapter whose drivers need updating : Go to the device properties, and in the 'Driver' tab, update the drivers.
- Restarting Your Adapter: Sometimes, a simple restart can work wonders. Right-click on the adapter and select "Disable device," then right-click again and choose "Enable device." This forces a reset.
Your WiFi adapter is like a loyal dog. Sometimes it just needs a little nudge to get back on track!
4. The Driver Dilemma: Missing or Outdated Drivers
Drivers are the software "translators" that allow your Windows 10 laptop to communicate with its hardware, including your WiFi adapter. If the drivers are missing, corrupted, or outdated, your WiFi might not function correctly.
- Updating Drivers: (We've already touched on this, but it's worth emphasizing). Go back to Device Manager (see section 3). Right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will try to find and install the latest drivers.
- Manual Driver Updates: If Windows can't find a driver, you might need to download it from your laptop manufacturer's website (Dell, HP, Lenovo, etc.). Search their support site for your laptop model and download the latest WiFi driver.
Why Drivers Matter: Drivers are the lifeblood of connectivity. Think of them as the secret sauce that makes everything work together smoothly.
5. The Forgotten Password Fumble: Double-Checking Your Credentials!
Sometimes, the solution is staring us right in the face. Have you recently changed your WiFi password? Or perhaps entered it incorrectly?
- Re-enter Your Password: Click on the WiFi icon in your system tray. Select your WiFi network and click "Connect." You'll be prompted to enter your password. Double-check for typos (caps lock, anyone?).
- Forget the Network and Reconnect: If you're still having trouble, try forgetting the network and re-entering the password. Right-click on the network name in the WiFi settings and choose "Forget." Then, select the network again and re-enter the password.
Password Protection: Password issues might seem obvious, but they're a common culprit. Don't let a simple typo keep you offline!
6. The Troubleshooter's Triumph: Letting Windows Do the Work!
Windows 10 includes a built-in troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common WiFi problems.
- Running the Troubleshooter: Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray. Select "Troubleshoot problems." Windows will scan for issues and try to resolve them.
- Following the Prompts: The troubleshooter will guide you through the process. It might suggest restarting your adapter, updating drivers, or other solutions.
The Troubleshooting Advantage: Consider this your digital mechanic – it can often identify and fix problems without you needing to get your hands dirty.
7. Router Reset Revelation: The Power of the Reboot!
Just like your laptop, your router can sometimes benefit from a good old-fashioned reboot. It's like a digital nap for your internet.
- Unplug and Wait: Unplug your router from the power outlet. Wait for at least 30 seconds (I usually go for a full minute just to be sure).
- Plug It Back In: Plug the router back in and wait for it to restart. This can take a few minutes.
- Test the Connection: After the router has fully restarted, try connecting your laptop to the WiFi again.
The Magic of Restarting: It genuinely works! Often a simple restart clears out temporary glitches and gets everything running smoothly again.
8. The IP Address Inquiries: Checking Your Network Settings
Your computer needs an IP address to communicate with the internet. Sometimes, your computer might not be getting one, or it might be conflicting with another device on your network.
- Obtain an IP Address Automatically: Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray and select "Open Network & Internet settings." Click on "Change adapter options." Right click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select properties. Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click properties. Enable "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically."
- Restart your Laptop: After making these changes, it's always a good idea to restart your laptop.
IP's Important Role: Your IP address is like your computer's digital mailing address. Without it, you can't receive or send online information!
9. Antenna Issues: Checking Your Laptop's Wireless Reception
Believe it or not, the physical position of your laptop can actually affect your WiFi signal!
- Physical Obstacles: Make sure there are no obstructions (walls, metal objects, other electronics) between your laptop and the router.
- Laptop Placement: Try moving your laptop closer to the router. Sometimes, simply moving your desk can resolve the issue.
- Antenna Hardware Issues : If your laptop's antenna has issues, this would be a hardware issue on your laptop's part. Contact your laptop's manufacturer.
The Strength of Location: Think of your WiFi signal as radio waves. Physical objects will impede the signals.
10. Firewall Frustration: Check Your Security Software
Firewalls (both the Windows firewall and any third-party security software) can sometimes block your WiFi connection.
- Temporarily Disable Firewall: Temporarily disable your firewall to see if it's the source of the problem. In the Windows search bar, search for "Windows
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit

By Howtosolveit How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
FIXED No WiFi Networks Found Windows 10

By Techworm FIXED No WiFi Networks Found Windows 10 by Techworm
Memperbaiki WiFi yang Tidak Muncul di Pengaturan Windows 11 Memperbaiki WiFi yang Hilang

By Sandeep Singh Memperbaiki WiFi yang Tidak Muncul di Pengaturan Windows 11 Memperbaiki WiFi yang Hilang by Sandeep Singh

Title: All But My WiFi Network Not Appeared Solved 2020
Channel: Simplify
All But My WiFi Network Not Appeared Solved 2020 by Simplify
Laptop Working
WiFi Vanished! Fix Your Windows 10 Laptop NOW!
Losing your WiFi connection on your Windows 10 laptop can feel like being stranded on a digital desert island. Suddenly, access to the internet, the lifeblood of modern productivity and communication, evaporates. Fear not, however! This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to resurrect your WiFi connection and get you back online with minimal frustration. We'll explore common culprits and offer precise solutions, ensuring your laptop’s connectivity blues become a distant memory.
1. The Initial Diagnosis: What Exactly Isn't Working?
Before diving into solutions, a clear understanding of the problem is crucial. Is your WiFi adapter completely missing? Does it show up in Device Manager with an error? Are you seeing the WiFi icon but encountering limited or no connectivity? Knowing the specific symptoms helps pinpoint the most effective solution. Consider what changed recently. Did you install a new program? Did Windows install an update? This information can be invaluable.
2. Checking the Physical Switch and Wireless Adapter Status
Let's start with the obvious. Many laptops have a physical switch, button, or keyboard shortcut (often using the Function (Fn) key in combination with another key like F2 or F12) to disable or enable the wireless adapter. Double-check this first. The switch might be inadvertently turned off.
Next, verify the status of your wireless adapter in Device Manager.
- Accessing Device Manager: Right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager." (Or, type "Device Manager" in the search bar and select the result.)
- Locating Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section. Here, you will see your WiFi adapter (e.g., "Intel Wireless-AC 9260" or "Qualcomm Atheros QCA9377").
- Interpreting the Status:
- If the adapter is missing: It’s a critical issue. It might be disabled, have driver problems, or there could be a hardware fault.
- If there's a yellow exclamation mark: This indicates a problem, often a driver issue.
- If there's a downward-pointing arrow: The adapter is disabled. Right-click and select "Enable device."
- If you see a red 'X': The device might be disabled, or there might be a conflicting configuration.
- If the adapter is listed and appears normal: Start by moving on to more complicated steps.
3. Driver Dilemmas: Updating, Reinstalling, and Troubleshooting
Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are frequent causes of WiFi woes in Windows 10.
- Updating Drivers Through Device Manager: Right-click your WiFi adapter in Device Manager, and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will search for and install the latest driver. Be patient while this is done.
- Manual Driver Updates: If the automatic update fails, visit the support website of your laptop manufacturer (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) or the manufacturer of your WiFi adapter (e.g., Intel, Realtek, Broadcom). Download the latest driver from there.
- Reinstalling Drivers: Sometimes, simply updating isn't enough. Right-click on the wireless adapter and select "Uninstall device," then follow the on-screen instructions. Restart your laptop. Windows should automatically install the appropriate driver. If not, install the driver you downloaded manually.
- Rolling Back Drivers: If the problems started after a driver update, right-click the adapter in Device Manager, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver."
4. Network Adapter Power Management Settings
Windows 10, by default, often conserves power by selectively disabling network adapters. This can sometimes cause the WiFi to disconnect or fail to connect.
- Adjusting Power Management Settings: In Device Manager, right-click the WiFi adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the option "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." Click "OK" and restart your laptop.
5. Addressing Network Service Conflicts and Problems
Certain Windows services are essential for WiFi functionality. Occasionally, these services might stop or encounter problems.
- Verifying and Restarting Crucial Services: Press
Win + R, typeservices.msc, and press Enter. Locate the following services:- "WLAN AutoConfig"
- "DHCP Client"
- "Network Connection Broker"
- "Network List Service"
- "Network Location Awareness"
- Checking Service Status: Double-click each service. Ensure the "Startup type" is set to "Automatic" or "Automatic (Delayed Start)." If the service isn't running, click "Start."
- Restarting Services: If any of these services seem problematic, restart them by right-clicking the service and selecting "Restart."
6. The Troubleshooter's Arsenal: Utilizing Windows 10's Built-In Tools
Windows 10 incorporates built-in troubleshooters that can automatically detect and resolve common network problems.
- Running the Network Troubleshooter: Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray (bottom-right corner of your screen) and select "Troubleshoot problems." The troubleshooter will guide you through a series of diagnostic steps.
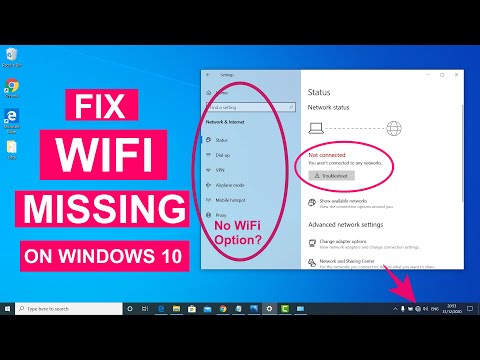
- Running the Internet Connections Troubleshooter: Go to "Settings" (accessed by typing "Settings" in the search bar), click "Network & Internet," and then click "Troubleshoot" under "Status."
- Running the Network Adapter Troubleshooter: In Device Manager (as described above), right-click the wireless adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Details" tab. In the "Property" dropdown, select "Troubleshooter," and begin to run the troubleshooter.
7. Network Reset: A Fresh Start for Your Network Configuration
A network reset restores your network settings to their default values, potentially resolving complex configuration issues. However, it will also remove and forget your saved WiFi Password.
- Performing a Network Reset: Go to "Settings," click "Network & Internet," and then click "Network reset" under "Status." Click "Reset now" and confirm. Your laptop will restart. After the restart, you will need to re-enter your WiFi password. You will have to reconnect to all saved networks.
8. Router-Related Troubleshooting: Beyond Your Laptop
Sometimes, the problem lies with your router, not your laptop.
- Restarting Your Router: This is the first step. Unplug your router and modem for 30 seconds before plugging them back in. Allow them to fully boot up.
- Checking Router Firmware: Ensure your router's firmware is up-to-date. Visit the router manufacturer's website to check for the latest version and instructions on how to update it.
- Router Channel Interference: WiFi routers operate on different channels. If your channel has too much interference from other networks (especially in crowded areas), the connection might be poor. Access your router's settings (usually by typing the router's IP address, often
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1, into your web browser) and change the WiFi channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are generally good starting points). - Router Security Settings: Verify your router’s security settings. Ensure the security protocol is set to WPA2-PSK or WPA3-PSK (if your devices support it) for the most secure and generally compatible option.
9. Firewall and Antivirus Interference
Your firewall or antivirus software could be blocking your WiFi connection.
- Temporarily Disabling the Firewall: Disable your Windows Firewall (for testing only) by going to "Settings," selecting "Update & Security," clicking "Windows Security," clicking "Firewall & network protection," and then disabling the firewall for "Private network" and "Public network." (Remember to re-enable it after testing.)
- Checking Antivirus Settings: Consult your antivirus software's documentation to learn how to configure it to allow network traffic. You might need to allow certain programs to access the network.
10. Hardware Considerations: When All Else Fails
If you've exhausted all software solutions, there might be a hardware issue.
- Internal WiFi Adapter Failure: It's the worst-case scenario, but the internal WiFi adapter may be failing. Professional repair or adapter replacement may be needed.
- External WiFi Adapters: If the adapter is removable, try taking it out and put it in again. Try another USB port.
- Laptop Hardware Issues: In rare cases, other hardware problems could be causing the WiFi issue. A professional inspection might be necessary.
- Consider an External WiFi Adapter: As a temporary or permanent fix, you can purchase an external USB WiFi adapter. They are inexpensive and easy to install.
11. Advanced Troubleshooting: Command Prompt and Registry Tweaks
These steps are for more advanced users. If you are not comfortable with the command prompt or registry editing, please carefully consider if you want to do these steps.
- Flushing the DNS Cache: Open Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd," right-click, and select "Run as administrator"). Type
ipconfig /flushdnsand
